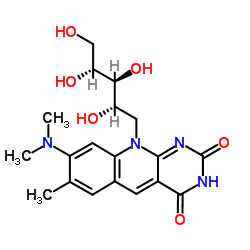
51093-55-1
| Name | roseoflavin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Roseoflavine
Riboflavin,8-demethyl-8-(dimethylamino) C18H23N5O6 8-Dimethylaminoriboflavin 8-(dimethylamino)-7-methyl-10-(2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentyl)benzo[g]pteridine-2,4-dione 7-Methyl-8-dimethylamino-10-(1'-D-ribityl)isoalloxazin 8-(dimethylamino)-7-methyl-10-((2S,3S,4R)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentyl)benzo[g]pteridine-2,4(3H,10H)-dione 8-demethyl-8-(dimethylamino)riboflavin 8-dimethylamino-7-methyl-10-D-ribitol-1-yl-10H-benzo[g]pteridine-2,4-dione 1-Deoxy-1-[8-(dimethylamino)-7-methyl-2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimido[4,5-b]quinolin-10(2H)-yl]-D-ribitol Roseoflavin |
| Description | Roseoflavin, a natural pigment originally isolated from Streptomyces davawensis, is an antimetabolite analog of Riboflavin and flavin mononucleotide that has antimicrobial properties[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Roseoflavin, a chemical analog of flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and riboflavin that has antimicrobial activity, can directly bind to FMN riboswitch (Kd~100 nM) aptamers and downregulate the expression of an FMN riboswitch-lacZ reporter gene in B. subtilis[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 276-278ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C18H23N5O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 404.417 |
| Exact Mass | 404.169586 |
| PSA | 151.91000 |
| LogP | -0.55 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.688 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|