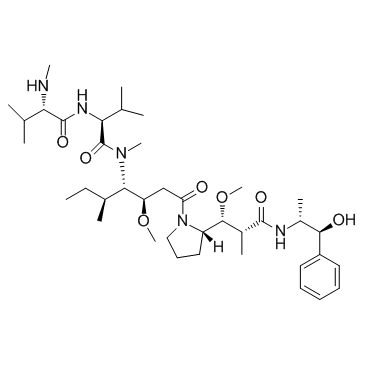
474645-27-7
| Name | [3H]-Vedotin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
MMAE
Monomethyl auristatin E Monomethylauristatin E UNII-V7I58RC5EJ monomethylauristatinE N-Methyl-L-valyl-N-[(3R,4S,5S)-1-{(2S)-2-[(1R,2R)-3-{[(1S,2R)-1-hydroxy-1-phenyl-2-propanyl]amino}-1-methoxy-2-methyl-3-oxopropyl]-1-pyrrolidinyl}-3-methoxy-5-methyl-1-oxo-4-heptanyl]-N-methyl-L-valinamide |
| Description | Monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) is a synthetic derivative of dolastatin 10 and functions as a potent mitotic inhibitor by inhibiting tubulin polymerization. MMAE is widely used as a cytotoxic component of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) to treat several different cancer types. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Microtubule[1] |
| In Vitro | Monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) is efficiently released from SGN-35 within CD30+ cancer cells and, due to its membrane permeability, is able to exert cytotoxic activity on bystander cells[1]. MMAE sensitizes colorectal and pancreatic cancer cells to IR in a schedule and dose dependent manner correlating with mitotic arrest. Radiosensitization is evidenced by decreased clonogenic survival and increased DNA double strand breaks in irradiated cells[2]. |
| In Vivo | Monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) in combination with IR results in tumor growth delay, tumor-targeted ACPP-cRGD-MMAE with IR produces a more robust and significantly prolongs tumor regression in xenograft models[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE, 5 nM) and ionizing radiation (IR) treated cells are harvested and lysed in RIPA buffer with protease and phosphatase inhibitors. Thirty μg of lysate undergo electrophoresis using 4-12% Bis-Tris gels, transferred to PVDF membranes and incubated with indicated primary antibodies. Blots are developed by ECL. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] 6-8 week old female athymic nu/nu mice are injected subcutaneously into thighs with 5×106 HCT-116 or PANC-1 cells in a 1:1 Matrigel and PBS solution. Mice are treated with IR or intravenous (IV) injection of ACPP-cRGD-MMAE (6 nmoles/day, 18 nmoles total, i.v.), tumor tissue is harvested, formalin fixed and paraffin embedded followed by staining with indicated antibodies. The primary antibody is used at a 1:250 dilution and is visualized using DAB as a chromagen with the UltraMap system. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 873.5±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C39H67N5O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 717.979 |
| Flash Point | 482.1±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 717.504028 |
| PSA | 149.54000 |
| LogP | 4.13 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.519 |