6754-20-7
| Name | polygodial |
|---|---|
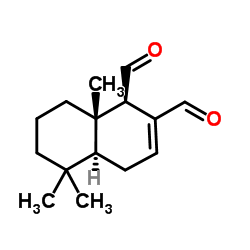
| Synonyms |
(1R,4aS,8aS)-5,5,8a-trimethyl-1,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-octahydronaphthalene-1,2-dicarbaldehyde
UNII:A00RAV0W57 Podofilox Wartec Condylox Podophyllotoxin 7 Condyline [1R-(1a,4ab,8aa)]-1,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-Octahydro-5,5,8a-trimethyl-1,2-naphthalenedicarboxaldehyde S-Isopropylisothiourea hydrobromide Polygodial Warticon (1R,4aS,8aS)-5,5,8a-Trimethyl-1,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-octahydro-1,2-naphthalenedicarbaldehyde Podophyllinic acid lactone |
| Description | Polygodial (Poligodial) is an antifungal potentiator[1]. Polygodial is a sesquiterpene with anti-hyperalgesic properties[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Polygodial exhibits fungicidal activity against Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Candida albicans, and other fungal pathogens in standardized susceptibility tests (NCCLS). Polygodial (12.5 μg/mL, 3 hours) induces significant shrinkage compared to controls in Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells with the minimum fungicidal concentration (MFC) for 106 CFU/mL in RPMI 1640 medium[3]. Cell Viability Assay[3] Cell Line: S. cerevisiae cells Concentration: 12.5 μg/mL Incubation Time: 3 hours Result: Treated cells exhibited significant shrinkage compared to controls, and the organization of subcellular organelles appears either disrupted or compacted. |
| In Vivo | Polygodial is a sesquiterpene isolated from the barks of Drymis winteri (Winteraceae). Polygodial (0.5 to 10 mg/kg; 0.5 h; given by i.p. route to mice) induces significant, dose-related and almost complete inhibition of Acetic acid, Kaolin and Zymosan-induced abdominal constrictions. The calculated mean ID50 values are 0.8, 2.1 and 2.6 mg/kg and maximal inhibitions of 90.0±3.0, 98.0±1.0 and 97.0±2.0 %, against Acetic acid, Kaolin and Zymosan, respectively. Polygodial is about 14- to 27-fold more potent than the hydroalcoholic extract (HE) at the ID50 level[2]. Animal Model: Non-fasted male Swiss mice (20-30 g) or male Wistar rats (150-180 g)[2] Dosage: 0.1 to 10 mg/kg Administration: Injected i.p. 0.5 h before the injection of irritant substances Result: Produced significant inhibition of Acetic acid, Kaolin and Zymosan-induced writhing in mice. |
| References |
[1]. I Kubo, et al. Polygodial, an antifungal potentiator. J Nat Prod. Jan-Feb 1988;51(1):22-9. |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 330.7±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C15H22O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 234.334 |
| Flash Point | 124.0±22.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 234.161987 |
| PSA | 34.14000 |
| LogP | 3.84 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.570 |
| Storage condition | 20°C |