55837-18-8
| Name | 2-[4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl]butanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Butibufenum [INN-Latin]
Butilopan 2-(p-Isobutylphenyl)butyrate 2-(4-isobutylphenyl)-butyric acid 2-(4-Isobutylphenyl)butanoic acid Butibufeno [INN-Spanish] EINECS 259-849-2 2-(4-Isobutylphenyl)buttersaeure Butibufen Butibufene [INN-French] |
| Description | Butibufen is a non-steroidal compound. Butibufen shows analgesic and antipyretic properties. Butibufen can be used for the research of inflammation[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Butibufen (0.1 μM-0.1 M; 60 min) affects cell viability and cell attachment with a high dose[2]. Butibufen (1 μM; 48 h) causes a 100% cell death after 48 h exposure[2]. Butibufen (2 μM-1 mM; 6 h) affects synthesis of albumin in hepatocytes[2]. Butibufen (0.2-0.4 mM; 6 h) impaires gluconeogenesis from lactate and significantly inhibited ureogenesis[2]. Cell Viability Assay[2] Cell Line: Hepatocytes from Sprague-Dawley male rats Concentration: 0.1 μM-0.1 M Incubation Time: 60 min Result: Showed no cell viability effects under the dose of 200 μM, but dose- and time-dependently affected cell viability with higher concentrations. |
| In Vivo | Butibufen (50 and 250 mg/kg; p.o. 8 and 3 h before sacrifice) affects acid phosphatase activity[3]. Animal Model: Sprague-Dawley rats[3] Dosage: 50 and 250 mg/kg Administration: Oral gavage; 50 and 250 mg/kg; 8 and 3 h before sacrifice Result: Reduced acid phosphatase activity but showed no effect on the stabilization of lysosomal membrane. |
| References |
| Density | 1.015g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 335.1ºC at 760mmHg |
| Melting Point | 51-53° |
| Molecular Formula | C14H20O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 220.30700 |
| Flash Point | 232.1ºC |
| Exact Mass | 220.14600 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 3.46330 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.515 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
|
~% 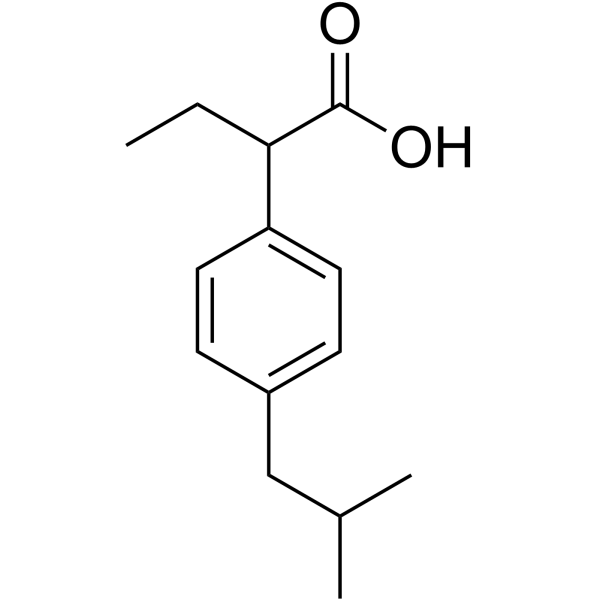
55837-18-8 |
| Literature: US4381313 A1, ; |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |