137975-06-5
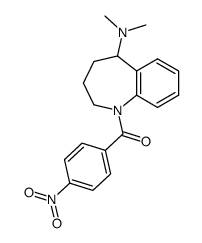
| Name | N-[4-[5-(dimethylamino)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1-benzazepine-1-carbonyl]phenyl]-2-methylbenzamide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
5-dimethylamino-1-[4-[(2-methylbenzoyl)amino]benzoyl]-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-benzazepine
N-(4-(((5RS)-5-(Dimethylamino)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-1-benzazepin-1-yl)carbonyl)phenyl)-2-methylbenzamide Mozavaptan Mozavaptan [INN] N-(4-((5-(Dimethylamino)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-1-benzazepin-1-yl)carbonyl)phenyl)-2-methylbenzamide (+/-)-5-dimethylamino-1-[4-(2-methylbenzoylamino)-benzoyl]-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-benzazepin Benzamide,N-(4-((5-(dimethylamino)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-1-benzazepin-1-yl)carbonyl)phenyl)-2-methyl N-(4-{[5-(Dimethylamino)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-1-benzazepin-1-yl]carbonyl}phenyl)-2-methylbenzamide |
| Description | Mozavaptan (OPC31260) is a orally effective, nonpeptide vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist with an IC50 of 14 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 14 nM (vasopressin receptor)[1] |
| In Vitro | Mozavaptan causes a competitive displacement of [3H]-arginine vasopressin (AVP) binding to both V1 and V2 receptors with IC50 values of 1.2 μM and 14 nM, respectively. The Kd of [3H]-AVP is reduced significantly in both rat liver and kidney in the presence of mozavaptan (Kd=1.1 nM in liver, Kd=1.38 nM in kidney)[1]. |
| In Vivo | Mozavaptan at doses of 10 to 100 μg/kg, i.v., inhibits the antidiuretic action of exogenously administered arginine vasopressin in water-loaded, alcohol-anaesthetized rats in a dose-dependent manner. Mozavaptan does not exert an antidiuretic activity suggesting that it is not a partial V2 receptor agonist. Mozavaptan dose-dependently increases urine flow and decreases urine osmolality after oral administration at doses of 1 to 30 mg/kg in normal conscious rats[1]. |
| Kinase Assay | To determine binding kinetic constants, liver or kidney plasma membranes are incubated with increasing concentrations of [3H]-AVP with or without excess (1 μM) unlabelled AVP to obtain a saturation curve. To investigate whether mozavaptan interacts competitively or noncompetitively, the saturation binding of [3H]-AVP is examined in the absence and presence of mozavaptan at concentrations of 0.3 μM and 1 μM in liver membranes and 3 nM, and 10 nM in kidney membranes. Data on the saturation curve are plotted according to the method of Scatchard and fitted by a regression analysis[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: Mozavaptan is dissolved in DMSO at a concentration of 10 mM and diluted with assay buffer. Female Brattleboro rats homozygous for hypothalamic diabetes insipidus and weighing between 180 and 280g are used. Mozavaptan (30 mg/kg) and vehicle (5% gum arabic) are administered orally in a volume of 2 mL/kg and d(CH2)5Tyr(Et)VAVP (10pgkg-1) is administered in a volume of 1 mL/kg. Spontaneously voided urine is collected for 6h with metabolic cages. Both before and during the study, the rats received water and food ad libitum[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 543.0±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C27H29N3O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 427.538 |
| Flash Point | 282.2±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 427.225983 |
| PSA | 52.65000 |
| LogP | 3.83 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.647 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
|
~52% 
137975-06-5 |
| Literature: Ogawa, Hidenori; Yamashita, Hiroshi; Kondo, Kazumi; Yamamura, Yoshitaka; Miyamoto, Hisashi; Kan, Keizo; Kitano, Kazuyoshi; Tanaka, Michinori; Nakaya, Kenji; Nakamura, Shigeki; Mori, Toyoki; Tominaga, Michiaki; Yabuuchi, Youichi Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1996 , vol. 39, # 18 p. 3547 - 3555 |
|
~% 
137975-06-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 39, # 18 p. 3547 - 3555 |
|
~% 
137975-06-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 39, # 18 p. 3547 - 3555 |
|
~% 
137975-06-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 39, # 18 p. 3547 - 3555 |
|
~% 
137975-06-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 39, # 18 p. 3547 - 3555 |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |