204512-90-3
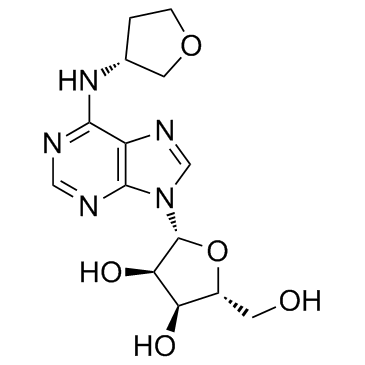
| Name | (2R,3S,4R,5R)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-5-[6-[[(3R)-oxolan-3-yl]amino]purin-9-yl]oxolane-3,4-diol |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Tecadenoson
N-(3-Tetrahydrofuranyl)-6-aminopurine riboside N-(3(R)-tetrahydrofuranyl)-6-aminopurine riboside 6-(N-3`-(R)-tetrahydrofuranyl)-amino-purine ribose Tecadenoson (USAN/INN) CVT-510 MFCD08690887 |
| Description | Tecadenoson (CVT-510) is a selective A1 adenosine receptor agonist. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Target: A1 adenosine receptor[1] |
| In Vitro | In the atrial-paced isolated heart, Tecadenoson is approximately 5 fold more potent to prolong the stimulus-to-His bundle (S-H interval), a measure of slowing AV nodal conduction (EC50=41 nM) than to increase coronary conductance (EC50=200 nM). At concentrations of Tecadenoson (40 nM) and diltiazem (1 μM) that causes equal prolongation of S-H interval (∼10 ms), diltiazem, but not Tecadenoson, significantly reduces left ventricular developed pressure (LVP) and markedly increases coronary conductance. Tecadenoson shortens atrial (EC50=73 nM) but not the ventricular monophasic action potentials (MAP)[1]. |
| In Vivo | In atrial-paced anaesthetized guinea-pigs, intravenous infusions of Tecadenoson and diltiazem causes nearly equal prolongations of P-R interval[1]. Tecadenoson (2, 5, 20 μg/kg i.p.) causes a rapid and sustained dose-dependent decrease in NEFA at doses that do not cause bradycardia. Tecadenoson given at 50 μg/kg causes a significant bradycardia (50% decrease in heart rate at 25 min[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | The effect of Tecadenoson on binding to A1 and A2A-adenosine receptors of porcine forebrain and striatum membranes, respectively, are determined. Assays for A1 and A2A receptors are carried out by using the A1 receptor antagonist [3H]CPX and the A2A receptor agonist [3H]CGS 21680. Membranes are treated with adenosine deaminase (2 U/mL) for 20 min at room temperature prior to and during radioligand binding assays. Membranes (0.2-0.7 mg), adenosine deaminase, and the indicated radioligand are incubated for 3 h in a 300 μL volume of Tris-HCl buffer (50 mM) (pH 7.4). Assays are carried out in triplicate at room temperature. After the incubation period, bound and free radioligand are diluted by the addition of ice-cold Tris-HCl buffer (5 mL), and immediately separated by vacuum filtration of assay contents onto Whatman GF/C filters and ishing of trapped membranes with Tris-HCl buffer (20 mL). Filter disks containing membrane-bound radioactivity are placed in 4 mL Scintiverse, and the radioactivity is quantified by a liquid scintillation counter. Specific binding of [3H]CPX and [3H]CGS 21680 is defined as membrane binding displaced in the presence of CPT (10 μM) and R-PIA (10 μM), respectively[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Rat: The effects of Tecadenoson on heart rate and to reduce serum NEFA concentration are determined in separate groups of rats to avoid the effects of animal handling and blood sampling on heart rate. Three days before an experiment, a catheter (0.025-mm outer diameter) is implanted in the left common carotid artery of each rat using aseptic conditions and sterile technique. The catheter is tunneled subcutaneously to the dorsal surface. After recovery from anesthesia, rats are placed in metabolic cages to facilitate handling and blood sampling. Blood samples (0.2 mL) are drawn before and at various time points after i.p. injection of either Tecadenoson or vehicle (DMSO in saline). A 0.4-mL volume of 1% sodium citrate in saline is administered after withdrawal of each blood sample to replace blood volume and prevent clotting in the carotid artery catheter. Serum is collected from each sample after centrifugation of the clotted blood. Serum samples are stored at −80°C until analysis. Serum NEFA concentration is determined using an enzymatic colorimetric assay kit[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.89g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 704.9ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C14H19N5O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 337.33100 |
| Flash Point | 380.1ºC |
| Exact Mass | 337.13900 |
| PSA | 134.78000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 7.4E-21mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.83 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |