17397-89-6
| Name | Cerulenin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
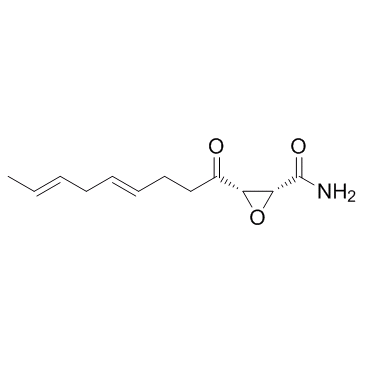
2,3-Epoxy-4-oxo-7,10-dodecadienamide
(2R,3S)-3-[(4E,7E)-Nona-4,7-dienoyl]oxirane-2-carboxamide trans-dodecadienamide) 3S)-2,3-epoxy-4-oxo-7,10-trans caerulein A EINECS 241-424-8 [2R-[2a,3a(4E,7E)]]-3-(1-Oxo-4,7-nonadienyl)oxiranecarboxamide Oxiranecarboxamide, 3-(1-oxo-4,7-nonadienyl)-, (2R-(2-α,3-α(4E,7E)))- (9CI) (2R,3S)-3-[(4E,7E)-4,7-Nonadienoyl]-2-oxiranecarboxamide Helicocerin MFCD00077686 (2R,3S)-3-[(4E,7E)-4,7-Nonadienoyl]-2-oxiranecarboximidic acid Cerulenin |
| Description | Cerulenin, the best known natural inhibitor of fatty acid synthase (FAS), is an epoxide produced by the fungus Cephalosporium caeruleus. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Fatty acid synthase (FAS)[1] |
| In Vitro | Cerulenin covalently binds to the catalytic site of FAS and disrupts the condensation reaction of acetyl-COA and malonyl-COA, inhibiting the biosynthesis of fatty acids and sterols in yeast. The Flavonoids quercetin and trans-Chalcone are effective against T. rubrum, with MICs of 125 and 7.5 μg/mL for the wild-type strain (MYA3108) and of 63 and 1.9 μg/mL for the ABC transporter mutant strain (ΔTruMDR2), respectively. The MICs of the Fluconazole and Cerulenin controls are 63 and 125 μg/mL for the wild-type strain and 30 and 15 μg/mL for the mutant strain, respectively[1]. To explore the underlying mechanism of Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR)’s protective effect on endothelial dysfunction model, the inhibitor of fatty acid synthase and HMG-CoA reductase, Cerulenin ( 5 μg/mL) and Lovastatin, are used before palmitic acid (PA) added. The mRNA expression of IL-1β, TNFα, VCAM-1 and IL-6 are reduced while NO production is recovered with inhibitor treatment[2]. |
| In Vivo | Cerulenin treatment of ob/ob mice has obvious effects on body weight. With 2 days of treatment, body weight in treated mice is decreased compared to a 5.7% weight gain in the controls. With prolonged (7 days) treatment, no body weight loss is observed, but body weight gain is slowed. In all groups, 60 mg/kg of Cerulenin is more effective than 30 mg/kg in inhibiting weight gain. If given daily or every other day, ATP content are increased 58.1% and 61.5% respectively by 7-day treatment of 60 mg/kg Cerulenin. Significant ATP elevation is also observed with only 2 days of treatment with 60 mg/kg Cerulenin. In contrast, 30 mg/kg Cerulenin, given either 2 or 7 days, does not show any significant effect on cellular ATP content[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Rat aortic endothelial cells (RAECs) are isolated and cultured with minor modifications. Briefly, segments of thoracic aorta are excised from male Wistar rats (150-180 g) and immediately placed in cold PBS containing 100 U/mL Penicillin and 100 mg/mL Streptomycin. The aorta is cut into 1 millimeter wide rings after the periadventitial fat is removed. Following transferred to a T-25 cm2 flasks, the rings are cultured in Medium 199 containing 20% fetal bovine serum, 2.5 ng/mL basic fibroblast growth factors, 100U/mL Penicillin and 100 mg/mL Streptomycin. The aorta rings are placed at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 for 72-80 h without movement. All pieces of aorta rings are removed when cells migrated. Its microvascular cytological characteristics are demonstrated by CD31 and vWF staining. In experiments involving PA treatment, M199 medium supplemented with 1% bovine serum albumin is used. All experiments are performed with RAECs up to passage 4. In the experiments with inhibitor, 5 μg/mL Cerulenin (in ethonal), or 5 μM Lovastatin (in DMSO), or 3.3 μg/mL Cerulenin plus 3.3 μM Lovastatin is added in culture media 24 hours prior to PA treatment. The same volume of solvents is added at the same time as control[2]. |
| Animal Admin | mice[3] Cerulenin is given to 6-8 week old male ob/ob mice in RPMI medium containing 20% DMSO intraperitoneally (i.p.). Controls are injected similarly with vehicle alone. The experimental groups (4 mice each) are as follows: A: 60 mg/kg/day Cerulenin, injected daily for 7 days; B: 60 mg/kg every other day for 7 days; C: 30 mg/kg/day for 7 days; D: 30 mg/kg every other day for 7 days; E: vehicle, daily for 7 days; F: 60 mg/kg/day Cerulenin for 2 days; G: 30 mg/kg/day Cerulenin for 2 days; H: vehicle, daily for 2 days; I: control. All animals are sacrificed on the same day under anesthesia. Blood is collected by portal vein puncture. Liver samples are snap-frozen in liquid N2 and stored at -80°C until analysis, or paraformaldehyde-fixed for histological analysis. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 456.1±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 93.5℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C12H17NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 223.268 |
| Flash Point | 241.1±25.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 223.120850 |
| PSA | 72.69000 |
| LogP | 0.94 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.529 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | 24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | JR1670000 |