2483831-72-5
| Name | Retinoic acid-d6 |
|---|
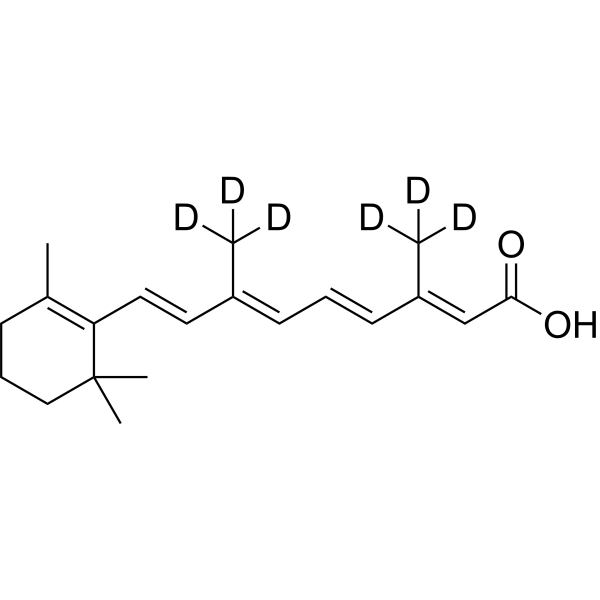
| Description | Retinoic acid-d6 is the deuterium labeled Retinoic acid[1]. Retinoic acid is a metabolite of vitamin A that plays important roles in cell growth, differentiation, and organogenesis. Retinoic acid is a natural agonist of RAR nuclear receptors, with IC50s of 14 nM for RARα/β/γ. Retinoic acid bind to PPARβ/δ with Kd of 17 nM. Retinoic acid acts as an inhibitor of transcription factor Nrf2 through activation of retinoic acid receptor alpha[2][3][4][5][6][7]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C20H22D6O2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 306.47 |