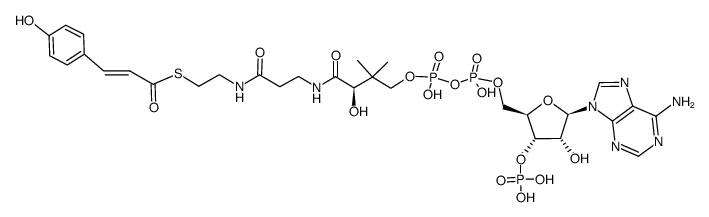
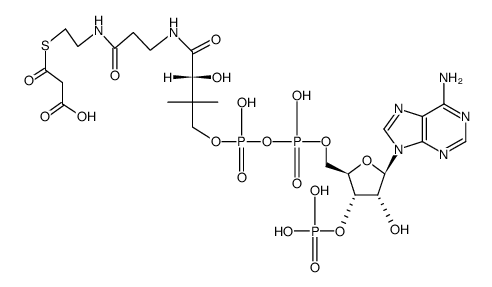
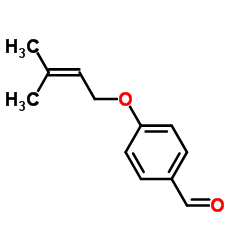
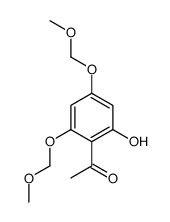
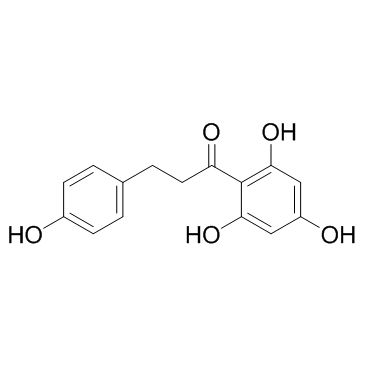
25515-46-2
| Name | Naringenin chalcone,2',4,4',6'-Tetrahydroxychalcone |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Isopropylammonium-N-isopropyl-dithiocarbaminat
isorpopylammonium N-isopropyldithiocarbamate propan-2-ylcarbamodithioic acid isosalipurpol trans-2',4',6',4-tetrahydroxychalcone chalconaringenin 6',4-tetrahydroxychalcone isopropylammonium N-isopropyldithiocarbamate ammonium isopropyldithiocarbamate |
| Description | (E)-Naringenin chalcone is an orally active anti-allergic agent. (E)-Naringenin chalcone also has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory activities. (E)-Naringenin chalcone can improve adipocyte functions. (E)-Naringenin chalcone inhibits histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cell[1][2][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | (E)-Naringenin chalcone (25-125 μg/mL, 10 min) inhibits histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells, with an IC50 value of 68 μg/mL[1]. (E)-Naringenin chalcone (25-50 μM, 8 days) improves adipocyte (3T3-L1) functions by enhancing adiponectin production[2]. (E)-Naringenin chalcone (25-100 μM, 24 h) stimulates the activity of PPARγ in NIH-3T3 cells[2]. (E)-Naringenin chalcone (0-200 μM 24 h) inhibits the production of TNF-alpha, MCP-1, and nitric oxide (NO) by LPS-stimulated RAW 264 macrophages[4]. RT-PCR[2] Cell Line: 3T3-L1 adipocytes Concentration: 25-100 μM Incubation Time: 8 days Result: Increased adiponectin mRNA levels up to 8.0-fold in a dose-dependent manner. Western Blot Analysis[4] Cell Line: RAW 264 macrophages Concentration: 0,25, 50, 100, 200 μM Incubation Time: 24 h Result: Suppressed the degradation of IκB-α. |
| In Vivo | (E)-Naringenin chalcone (0.8 mg/kg, oral administration) shows anti-allergic effect in type I allergic mice[1]. (E)-Naringenin chalcone (0.8 mg/kg, oral administration) suppresses allergic asthma by inhibiting the type-2 function of CD4 T cells in allergic airway inflammatory mice[3]. Animal Model: Mouse type I allergic model[1] Dosage: 0.8 mg/kg Administration: Oral administration Result: Inhibited the ear-swelling response, with the inhibitory ratio of 46.7%. Animal Model: Allergic airway inflammation induced in mice[3] Dosage: 0.8 mg/kg Administration: Oral administration, daily Result: Decreased cell numbers of the infiltrating leukocyte and eosinophils. Decreased Muc5ac and gob-5 expression in the lungs. |
| References |
| Density | 1.483±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 538.7±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Molecular Formula | C15H12O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 272.25300 |
| Exact Mass | 272.06800 |
| PSA | 97.99000 |
| LogP | 2.40510 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
|
~80% 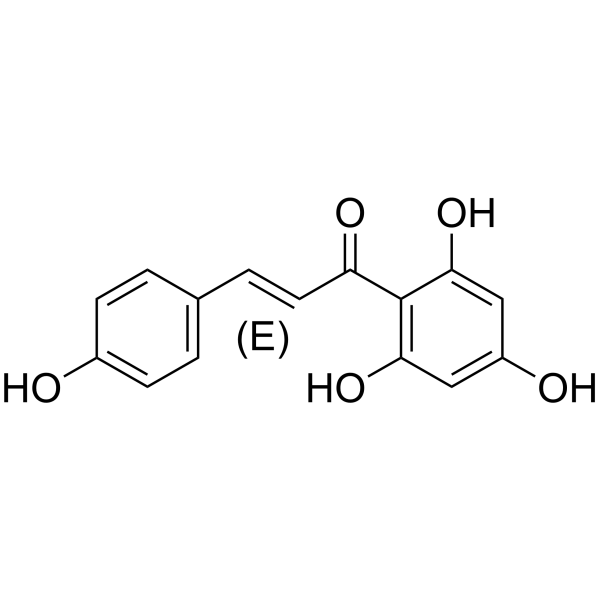
25515-46-2 |
| Literature: Stompor, Monika; Potaniec, Bartomiej; Szumny, Antoni; Zielinski, Pawe; Zonierczyk, Anna Katarzyna; Aniol, Miroslaw Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 2013 , vol. 97, p. 283 - 288 |
|
~% 
25515-46-2 |
| Literature: Sogawa; Nihro; Ueda; Izumi; Miki; Matsumoto; Satoh Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1993 , vol. 36, # 24 p. 3904 - 3909 |
|
~% 
25515-46-2 |
| Literature: Sogawa; Nihro; Ueda; Izumi; Miki; Matsumoto; Satoh Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1993 , vol. 36, # 24 p. 3904 - 3909 |
|
~% 
25515-46-2 |
| Literature: Sogawa; Nihro; Ueda; Izumi; Miki; Matsumoto; Satoh Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1993 , vol. 36, # 24 p. 3904 - 3909 |
|
~% 
25515-46-2 |
| Literature: Abe, Ikuro; Oguro, Satoshi; Utsumi, Yoriko; Sano, Yukie; Noguchi, Hiroshi Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2005 , vol. 127, # 36 p. 12709 - 12716 |
|
~% 
25515-46-2 |
| Literature: Kenez, Agnes; Juhasz, Laszlo; Antus, Sandor Heterocyclic Communications, 2002 , vol. 8, # 6 p. 543 - 548 |
|
~% 
25515-46-2 |
| Literature: Kenez, Agnes; Juhasz, Laszlo; Antus, Sandor Heterocyclic Communications, 2002 , vol. 8, # 6 p. 543 - 548 |
|
~% 
25515-46-2 |
| Literature: Abe, Tsuyoshi; Noma, Hisashi; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Abe, Ikuro Tetrahedron Letters, 2006 , vol. 47, # 49 p. 8727 - 8730 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |