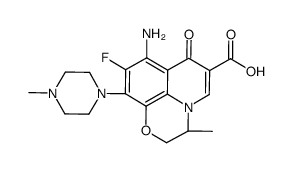
119354-43-7
| Name | (S)-Antofloxacin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
7H-Pyrido(1,2,3-de)-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic acid,8-amino-9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-,(3S)
UNII-56A192VX1Q Antofloxacin |
| Description | Antofloxacin is a well tolerate, orally active and broad-spectrum 8-amino-fluoroquinolone with potent antibacterial activities. Antofloxacin shows superior antibacterial activity against gyrA mutation-positive H. pylori strains, especially in Asn87- mutated strains, compared to levofloxacin. Antofloxacin is a weak, reversible inhibitor of CYP1A2 for the treatment of infections caused by a diverse group of bacterial species[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Bacterial[1][2] |
| In Vivo | Antofloxacin (2.5~160 mg/kg; s.c.; 24 hours) penetration ratio ranges from 1.22 to 1.54 for the total drug concentrations and is independent of the dose levels[3].Antofloxacin increases the plasma theophylline concentration, partly by acting as a mechanism based inhibitor of CYP1A2. Antofloxacin inhibits the formation of the three metabolites of theophylline was time-, concentration- and NADPH-dependent, which is characteristic of mechanism-based inhibition[2]. Animal Model: Mice[3] Dosage: 2.5~160 mg/kg (Pharmacokinetic Analysis) Administration: S.c.; 24 hours Result: Penetration ratio ranged from 1.22 to 1.54 for the total drug concentrations and was independent of the dose levels. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C18H21FN4O4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 376.38200 |
| Exact Mass | 376.15500 |
| PSA | 101.03000 |
| LogP | 1.71030 |