Structure-release relationships of physically based polymer-biocide combinations. Part 3: Effect of the environment on the release of 3(5)-methylpyrazole from monolithic matrix systems.
B Schulz, M Hartmann
Index: Pharmazie 43(1) , 29-31, (1988)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The release behaviour of the antimicrobially active 3(5)-methylpyrazole from matrix systems prepared from maleic anhydride copolymers as well as from copolymers of maleic esters and maleic amides was studied. Under alkaline conditions erosion is the predominant release mechanism compared to the release of the agent by diffusion into neutral or acid media. The presence of potassium and calcium salts influences the release rate under aquatic conditions in a different way. The diffusion rate of the active ingredient through membranes of maleic anhydride copolymers also depends on interactions with the surrounding media as well as on the hydrophilicity of the matrix.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
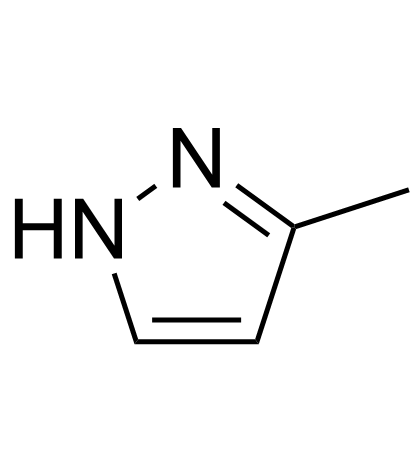 |
3-Methylpyrazole
CAS:1453-58-3 |
C4H6N2 |
|
[Toxicological evaluation of a new nitrification inhibitor a...
1986-06-01 [Gig. Sanit. (6) , 29-31, (1986)] |
|
Differential effects of 4-iodopyrazole and 3-methylpyrazole ...
1987-01-01 [J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 113(2) , 145-50, (1987)] |
|
Extremely long protection by pyrazole derivatives against ch...
1991-02-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 256(2) , 592-8, (1991)] |
|
[Structure-release relationships of active polymeric drug co...
1985-08-01 [Pharmazie 40(8) , 548-52, (1985)] |
|
[Structure-release relationship of physical polymer/drug com...
1986-02-01 [Pharmazie 41(2) , 118-20, (1986)] |