Functional assessment of four types of disintegrants and their effect on the spironolactone release properties.
John Rojas, Santiago Guisao, Vanesa Ruge
Index: AAPS PharmSciTech 13(4) , 1054-62, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Spironolactone is a drug derived from sterols that exhibits an incomplete oral absorption due to its low water solubility and slow dissolution rate. In this study, formulations of spironolactone with four disintegrants named as croscarmellose sodium, crospovidone, sodium starch glycolate and microcrystalline cellulose II (MCCII) were conducted. The effect of those disintegrants on the tensile strength, disintegration time and dissolution rate of spironolactone-based compacts was evaluated using a factorial design with three categorical factors (filler, lubricant, and disintegrant). The swelling values, water uptake and water sorption studies of these disintegrants all suggested that MCCII compacts disintegrate by a wicking mechanism similar to that of crospovidone, whereas a swelling mechanism was dominant for sodium starch glycolate and croscarmellose sodium. The disintegration time of MCCII and sodium starch glycolate remained unchanged with magnesium stearate. However, this lubricant delayed the disintegration time of crospovidone and croscarmellose sodium. MCCII presented the fastest disintegration time independent of the medium and lubricant employed. The water sorption ratio and swelling values determined sodium starch glycolate followed by croscarmellose sodium as the largest swelling materials, whereas crospovidone and MCCII where the least swelling disintegrants. The swelling property of sodium starch glycolate and croscarmellose sodium was strongly affected by the medium pH. The disintegration time of spironolactone compacts was faster when starch was used as a filler due to the formation of soft compacts. In this case, the type of filler employed rather than the disintegrant had a major effect on the disintegration and dissolution times of spironolactone.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
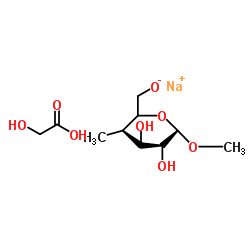 |
Sodium carboxyl methylstarch
CAS:9063-38-1 |
C10H19NaO8 |
|
II. Technological approaches to improve the dissolution beha...
2013-09-15 [Int. J. Pharm. 454(1) , 568-72, (2013)] |
|
Ultrasonic approach for viscoelastic and microstructure char...
2013-09-15 [Int. J. Pharm. 454(1) , 333-43, (2013)] |
|
Preparation of cross-linked carboxymethyl jackfruit starch a...
2011-10-01 [Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 24(4) , 415-20, (2011)] |
|
Dissolution rate enhancement of gliclazide by ordered mixing...
2011-09-01 [Acta. Pharm. 61(3) , 323-34, (2011)] |
|
Development and optimization of dextromethorphan hydrobromid...
2013-01-01 [Pharm. Dev. Technol. 18(2) , 454-63, (2013)] |