Deglycosylation of flavonoid and isoflavonoid glycosides by human small intestine and liver beta-glucosidase activity.
A J Day, M S DuPont, S Ridley, M Rhodes, M J Rhodes, M R Morgan, G Williamson
Index: FEBS Lett. 436(1) , 71-5, (1998)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Flavonoid and isoflavonoid glycosides are common dietary phenolics which may be absorbed from the small intestine of humans. The ability of cell-free extracts from human small intestine and liver to deglycosylate various (iso)flavonoid glycosides was investigated. Quercetin 4'-glucoside, naringenin 7-glucoside, apigenin 7-glucoside, genistein 7-glucoside and daidzein 7-glucoside were rapidly deglycosylated by both tissue extracts, whereas quercetin 3,4'-diglucoside, quercetin 3-glucoside, kaempferol 3-glucoside, quercetin 3-rhamnoglucoside and naringenin 7-rhamnoglucoside remained unchanged. The Km for hydrolysis of quercetin 4'-glucoside and genistein 7-glucoside was approximately 32+/-12 and approximately 14+/-3 microM in both tissues respectively. The enzymatic activity of the cell-free extracts exhibits similar properties to the cytosolic broad-specificity -glucosidase previously described in mammals.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
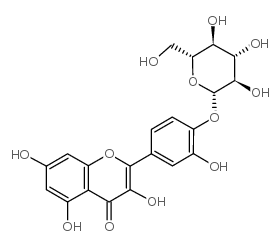 |
spiraeoside
CAS:20229-56-5 |
C21H20O12 |
|
The crystal structure of human cytosolic beta-glucosidase un...
2007-07-27 [J. Mol. Biol. 370(5) , 964-75, (2007)] |
|
Flavonoid glycosides inhibit oral cancer cell proliferation-...
2005-08-01 [J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 57(8) , 1037-42, (2005)] |
|
Quercetin glucosides inhibit glucose uptake into brush-borde...
2004-06-01 [Br. J. Nutr. 91(6) , 849-55, (2004)] |
|
Disposition and metabolism of [2-14C]quercetin-4'-glucoside ...
2005-07-01 [Drug Metab. Dispos. 33(7) , 1036-43, (2005)] |
|
Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of quercetin glycosides...
2001-05-01 [J. Clin. Pharmacol. 41(5) , 492-9, (2001)] |