DNA adducts from nitroreduction of 2,7-dinitrofluorene, a mammary gland carcinogen, catalyzed by rat liver or mammary gland cytosol.
Clare L Ritter, Sandra J Culp, James P Freeman, M Matilde Marques, Frederick A Beland, Danuta Malejka-Giganti
Index: Chem. Res. Toxicol. 15(4) , 536-44, (2002)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Nitrofluorenes are mutagenic and carcinogenic environmental pollutants arising chiefly from combustion of fossil fuels. Nitro aromatic compounds undergo nitroreduction to N-hydroxy arylamines that bind to DNA directly or after O-esterification. This study analyzes the DNA binding and adducts from the in vitro nitroreduction of 2,7-dinitrofluorene (2,7-diNF), a potent mammary carcinogen in the rat. Potential adduct(s) of 2,7-diNF was (were) generated by reduction of 2-nitroso-7-NF with ascorbate/H(+) in the presence of calf thymus DNA. The major adduct was characterized by HPLC/ESI/MS and (1)H NMR spectrometry as N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-2-amino-7-NF, and a minor one was determined by HPLC/ESI/MS to be a deoxyadenosine adduct of 2-amino-7-NF. Products from enzymatic nitroreduction were monitored by HPLC and DNA adduct formation by (32)P-postlabeling. Xanthine oxidase/hypoxanthine-catalyzed nitroreduction of 2,7-diNF, 2-nitrofluorene (2-NF), and 1-nitropyrene (1-NP) yielded the respective amines to similar extents (30-50%). However, the level of the major adducts ( approximately 0.15/10(6) nucleotides) from 2-NF [N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-2-aminofluorene] and 2,7-diNF [N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-2-amino-7-NF] was < or = 2% that from 1-NP. In the presence of acetyl CoA, nitroreduction of 2-NF catalyzed by rat liver cytosol/NADH yielded the same adduct at a level of 2.2/10(6) nucleotides. Liver or mammary gland cytosol with acetyl CoA yielded mainly N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-2-amino-7-NF from 2,7-diNF at >30 adducts/10(6) nucleotides, levels comparable to those from 1,6-dinitropyrene and 4- or 49-fold greater than the respective levels without acetyl CoA. Recovery of 2-nitroso-7-NF and 2-amino-7-NF from cytosol-catalyzed reduction of 2,7-diNF indicated nitroreduction and an N-hydroxy arylamine intermediate. Likewise, the presence of 2-acetylamino-7-NF indicated that reactivity with acyltransferase(s) was not prevented by the nitro group at C7. These data are consistent with activation of 2,7-diNF via nitroreduction to the N-hydroxy arylamine and acetyl CoA-dependent O-acetylation of the latter to bind to DNA. Enzymatic nitroreduction of 2,7-diNF was greatly enhanced by 9-oxidation. The nitroreduction of either 9-oxo-2,7-diNF or 9-hydroxy-2,7-diNF catalyzed by liver cytosol with acetyl CoA yielded two adducts (>2/10(6) nucleotides). Differences in the TLC migration of these adducts, compared to those from 2,7-diNF, and the lack of 2,7-diNF formation in the incubations suggested retention of the C9-oxidized groups. The relative ratios of the amine to amide from nitroreductions of 9-oxo-2,7-diNF and 2,7-diNF catalyzed by liver cytosol suggested that the 9-oxo group decreased reactivity with acyltransferase and, thus, the amount of N-acetoxy arylamine that binds to DNA. The mammary gland tumorigenicity of 2,7-diNF and the extent of its activation by the tumor target tissue shown herein suggest relevance of this environmental pollutant for breast cancer.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
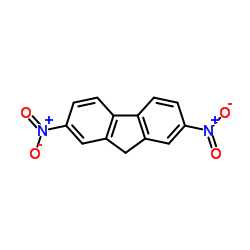 |
2,7-dinitro-9H-fluorene
CAS:5405-53-8 |
C13H8N2O4 |
|
Voltammetric detection of damage to DNA caused by nitro deri...
2010-05-01 [Anal. Bioanal. Chem 397(1) , 233-41, (2010)] |
|
Preneoplastic lesions and DNA adduct formation of the airbor...
1993-12-01 [Carcinogenesis 14(12) , 2627-32, (1993)] |
|
Reductions of nitro and 9-Oxo groups of environmental nitrof...
2000-08-01 [Chem. Res. Toxicol. 13(8) , 793-800, (2000)] |
|
Potent carcinogenicity of 2,7-dinitrofluorene, an environmen...
1999-10-01 [Carcinogenesis 20(10) , 2017-23, (1999)] |
|
Tumorigenicity and genotoxicity of an environmental pollutan...
2008-05-01 [Int. J. Cancer 122(9) , 1958-65, (2008)] |