| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Deoxyribonucleic acids, thymus gland, sodium salts
CAS:73049-39-5 |
|
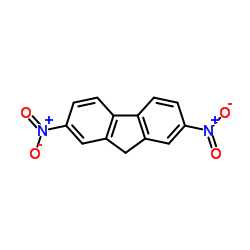 |
2,7-dinitro-9H-fluorene
CAS:5405-53-8 |
|
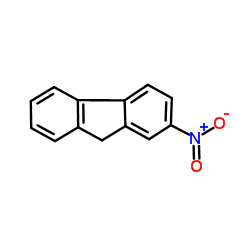 |
2-Nitro-9H-fluorene
CAS:607-57-8 |