| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
OR-486
CAS:7659-29-2 |
|
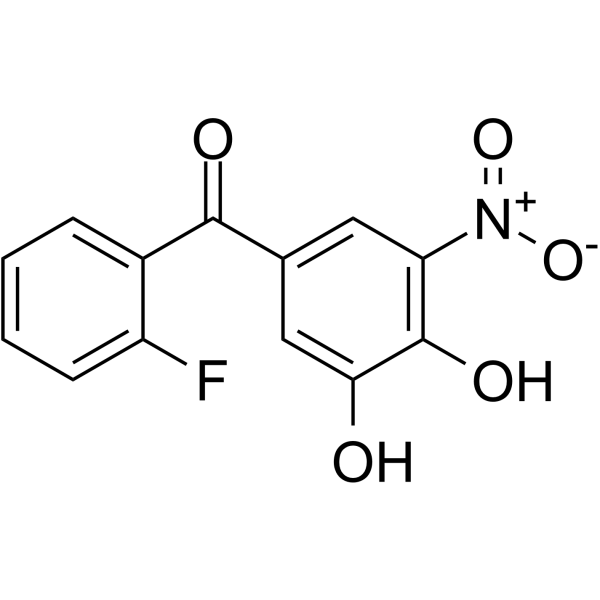 |
Ro 41-0960
CAS:125628-97-9 |