| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Deoxyribonucleic acids, thymus gland, sodium salts
CAS:73049-39-5 |
|
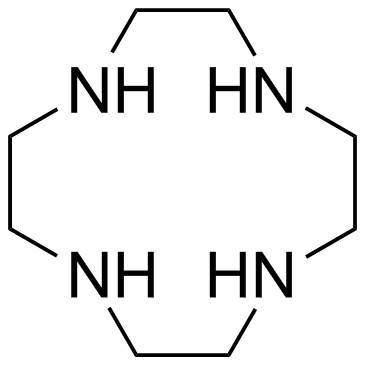 |
Cyclen
CAS:294-90-6 |