Inhibitory mechanisms of antibiotics targeting elongation factor Tu.
T Hogg, J R Mesters, R Hilgenfeld
Index: Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 3(1) , 121-31, (2002)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Since the pioneering discovery of the inhibitory effects of kirromycin on bacterial elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu) more than 25 years ago [1], a great wealth of biological data has accumulated concerning protein biosynthesis inhibitors specific for EF-Tu. With the subsequent discovery of over two dozen naturally occurring EF-Tu inhibitors belonging to four different subclasses, EF-Tu has blossomed into an appealing antimicrobial target for rational drug discovery efforts. Very recently, independent crystal structure determinations of EF-Tu in complex with two potent antibiotics, aurodox and GE2270A, have provided structural explanations for the mode of action of these two compounds, and have set the foundation for the design of inhibitors with higher bioavailability, broader spectra, and greater efficacy.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
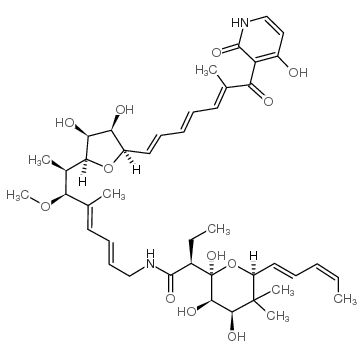 |
Kirromycin
CAS:50935-71-2 |
C43H60N2O12 |
|
A signal relay between ribosomal protein S12 and elongation ...
2009-02-01 [RNA 15(2) , 208-14, (2009)] |
|
The phosphopantetheinyl transferase KirP activates the ACP a...
2011-06-01 [FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 319(1) , 26-33, (2011)] |
|
Thermodynamic properties of nucleotide-free EF-Tu from Therm...
2002-05-20 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1597(1) , 22-7, (2002)] |
|
G13A substitution affects the biochemical and physical prope...
2002-01-15 [Biochemistry 41(2) , 628-33, (2002)] |
|
The kirromycin gene cluster of Streptomyces collinus Tü 365 ...
2009-08-01 [J. Antibiot. 62(8) , 465-8, (2009)] |