Urinary monohydroxy bile acids in young infants with obstructive jaundice.
Y Tazawa, T Konno
Index: Acta Paediatr. Scand. 71(1) , 91-5, (1982)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Using an aluminum oxide column, we fractionated and quantitatively determined urinary monohydroxy bile acids in young infants. For comparison purposes, monohydroxy bile acids were also measured in urine from older children and adults with obstructive jaundice. Lithocholic acid was not found in any specimens of the young infants examined, while 3 beta-hydroxy-5-cholenoic acid was detected in all. In the biliary atresia group, 3 beta-hydroxy-5-cholenoic acid excreted was 0.45+/-0.28 mumol per day (n=7), and in the neonatal hepatitis group, 0.48+/-0.44 mumol per day (n=9). The mean rate of 3 beta-hydroxy-5-cholenoic acid to total urinary bile acids in the biliary atresia group was 2.1%, and 1.3% in the neonatal hepatitis group. In the older children and adults with obstructive jaundice (n=6), 3 beta-hydroxy-5-cholenoic acid was excreted at a mean rate of 3.9% of total urinary bile acids, ranging from 0.63 to 14.81 mol per day. The excretion rate of 3 beta-hydroxy-5-cholenoic acid was related to that of chenodeoxycholic acid (p less than 0.05) in infants, while it was related to that of both chenodeoxycholic acid (p less than 0.01) and cholic acid (p less than 0.05) in older children and adults.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
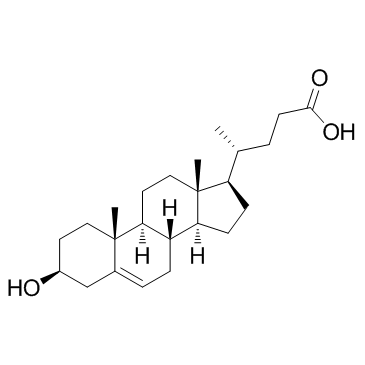 |
3b-Hydroxy-5-cholenoic acid
CAS:5255-17-4 |
C24H38O3 |
|
Hepatic bile salt sulfotransferases in the rat: sulfation of...
1991-02-01 [J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 12(2) , 260-8, (1991)] |
|
Determination of 3 beta-hydroxy-5-cholen-24-oic acid and its...
1984-07-01 [Steroids 44(1) , 47-55, (1984)] |
|
Unusual serum bile acid pattern in children with the syndrom...
1985-02-15 [Clin. Chim. Acta 145(3) , 289-96, (1985)] |
|
Purification and properties of a novel sulfatase from Pseudo...
1998-09-01 [Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 62(9) , 1739-44, (1998)] |
|
Preparation and antigenic property of methyl 3 beta-hydroxy-...
1983-02-01 [Steroids 41(2) , 155-64, (1983)] |