Purification and properties of a novel sulfatase from Pseudomonas testosteroni that hydrolyzed 3 beta-hydroxy-5-cholenoic acid 3-sulfate.
Y Tazuke, K Matsuda, K Adachi, Y Tsukada
Index: Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 62(9) , 1739-44, (1998)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A novel sulfatase hydrolyzing the sulfate ester bond in 3 beta-hydroxy-5-cholenoic acid 3-sulfate (delta 5-3 beta-sulfate) was purified from Pseudomonas testosteroni ATCC 11996 as the second bile acid sulfatase. The molecular weight was 95,000 and the molecule was composed of a homodimer of a subunit of which the molecular weight was 46,000. This sulfatase hydrolyzed delta 5-3 beta-sulfate to 3 alpha-hydroxy-5-cholenoic acid and sulfuric acid with inversion of beta- to alpha-configuration of the hydroxyl group at the C-3 position of the substrate. The optimum pH and the stable pH of the enzyme were 8.5 and 6.5-9.7, respectively. 3 beta-Sulfate ester bonds of steroids such as isolithocholic acid, pregnenolone, and epiandrosterone, in which the side chain of the steroid ring was shorter than cholesterol, were also hydrolyzed to 3 alpha-hydroxyl compounds corresponding to each steroid compound and sulfuric acid. We tentatively named this novel enzyme bile acid 3 beta-sulfate sulfohydrolase (beta-BSS).
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
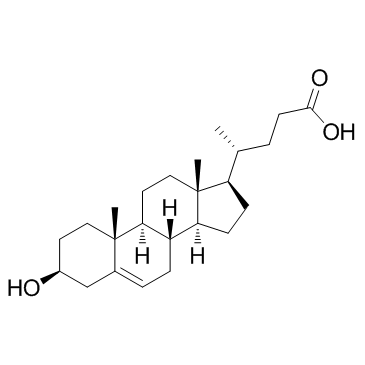 |
3b-Hydroxy-5-cholenoic acid
CAS:5255-17-4 |
C24H38O3 |
|
Hepatic bile salt sulfotransferases in the rat: sulfation of...
1991-02-01 [J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 12(2) , 260-8, (1991)] |
|
Determination of 3 beta-hydroxy-5-cholen-24-oic acid and its...
1984-07-01 [Steroids 44(1) , 47-55, (1984)] |
|
Unusual serum bile acid pattern in children with the syndrom...
1985-02-15 [Clin. Chim. Acta 145(3) , 289-96, (1985)] |
|
Preparation and antigenic property of methyl 3 beta-hydroxy-...
1983-02-01 [Steroids 41(2) , 155-64, (1983)] |
|
Metabolism of 27-, 25- and 24-hydroxycholesterol in rat glia...
1997-02-15 [Biochem. J. 322 ( Pt 1) , 175-84, (1997)] |