Chrysamine-G binding to Alzheimer and control brain: autopsy study of a new amyloid probe.
W E Klunk, M L Debnath, J W Pettegrew
Index: Neurobiol. Aging 16(4) , 541-8, (1995)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Chrysamine-G (CG) is a carboxylic acid analogue of Congo red, a histologic dye which stains amyloid. CG binds to the beta-amyloid protein of Alzheimer's disease (AD) in vitro and partitions into the brain of normal mice. In this study, we demonstrate increased binding of [14C]CG to homogenates of several regions of AD brain as compared to control. The total binding of CG to AD brain was approximately two- to three-fold that of control brain. The cerebellum could be used as an internal standard for each brain as CG binding to cerebellum did not differ between AD and control. The binding of [14C]CG correlated with numbers of senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. In addition, CG could be used to stain cerebrovascular amyloid in tissue sections. These results suggest that CG may prove useful as an in vivo probe of amyloid deposition in AD.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
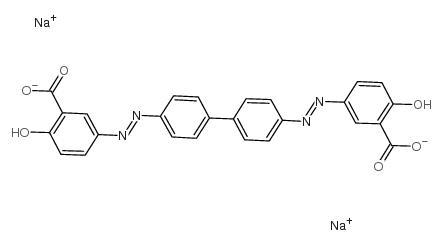 |
CHRYSAMINE G
CAS:6472-91-9 |
C26H16N4Na2O6 |
|
Imaging Abeta plaques in living transgenic mice with multiph...
2002-09-01 [J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 61 , 797-805, (2002)] |
|
Amyloid binding ligands as Alzheimer's disease therapies.
2002-01-01 [Neurobiol. Aging 23 , 1039-1042, (2002)] |
|
Chrysamine G and its derivative reduce amyloid beta-induced ...
2002-11-15 [Neurosci. Lett. 333 , 5-8, (2002)] |
|
99mTc-MAMA-chrysamine G, a probe for beta-amyloid protein of...
1999-11-01 [Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 26(11) , 1392-9, (1999)] |
|
Inhibition of polyglutamine aggregation in R6/2 HD brain sli...
2001-12-01 [Neurobiol. Dis. 8(6) , 1017-26, (2001)] |