Inhibition of polyglutamine aggregation in R6/2 HD brain slices-complex dose-response profiles.
D L Smith, R Portier, B Woodman, E Hockly, A Mahal, W E Klunk, X J Li, E Wanker, K D Murray, G P Bates
Index: Neurobiol. Dis. 8(6) , 1017-26, (2001)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Huntington's disease (HD) is a late onset neurodegenerative disorder caused by a CAG/polyglutamine (polyQ) repeat expansion. PolyQ aggregates can be detected in the nuclei and processes of neurons in HD patients and mouse models prior to the onset of symptoms. The misfolding and aggregation pathway is an important therapeutic target. To better test the efficacy of aggregation inhibitors, we have developed an organotypic slice culture system. We show here that the formation of polyQ aggregates in hippocampal slices established from the R6/2 mouse follows the same prescribed sequence as occurs in vivo. Using this assay, we show that Congo red and chrysamine G can modulate aggregate formation, but show complex dose-response curves. Oral administration of creatine has been shown to delay the onset of all aspects of the phenotype and neuropathology in R6/2 mice. We show here that creatine can similarly inhibit aggregate formation in the slice culture assay.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
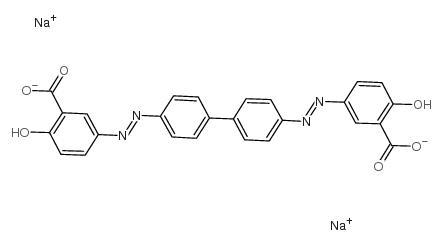 |
CHRYSAMINE G
CAS:6472-91-9 |
C26H16N4Na2O6 |
|
Imaging Abeta plaques in living transgenic mice with multiph...
2002-09-01 [J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 61 , 797-805, (2002)] |
|
Amyloid binding ligands as Alzheimer's disease therapies.
2002-01-01 [Neurobiol. Aging 23 , 1039-1042, (2002)] |
|
Chrysamine G and its derivative reduce amyloid beta-induced ...
2002-11-15 [Neurosci. Lett. 333 , 5-8, (2002)] |
|
99mTc-MAMA-chrysamine G, a probe for beta-amyloid protein of...
1999-11-01 [Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 26(11) , 1392-9, (1999)] |
|
In vitro drug treatments reduce the deleterious effects of a...
2012-01-01 [Neurobiol. Dis. 45 , 508-18, (2012)] |