Imaging Abeta plaques in living transgenic mice with multiphoton microscopy and methoxy-X04, a systemically administered Congo red derivative.
William E Klunk, Brian J Bacskai, Chester A Mathis, Stephen T Kajdasz, Megan E McLellan, Matthew P Frosch, Manik L Debnath, Daniel P Holt, Yanming Wang, Bradley T Hyman
Index: J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 61 , 797-805, (2002)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The identification of amyloid deposits in living Alzheimer disease (AD) patients is important for both early diagnosis and for monitoring the efficacy of newly developed anti-amyloid therapies. Methoxy-X04 is a derivative of Congo red and Chrysamine-G that contains no acid groups and is therefore smaller and much more lipophilic than Congo red or Chrysamine-G. Methoxy-X04 retains in vitro binding affinity for amyloid beta (Abeta) fibrils (Ki = 26.8 nM) very similar to that of Chrysamine-G (Ki = 25.3 nM). Methoxy-X04 is fluorescent and stains plaques, tangles, and cerebrovascular amyloid in postmortem sections of AD brain with good specificity. Using multiphoton microscopy to obtain high-resolution (1 microm) fluorescent images from the brains of living PSI/APP mice, individual plaques could be distinguished within 30 to 60 min after a single i.v. injection of 5 to 10 mg/kg methoxy-X04. A single i.p. injection of 10 mg/kg methoxy-X04 also produced high contrast images of plaques and cerebrovascular amyloid in PSI/APP mouse brain. Complementary quantitative studies using tracer doses of carbon- 11-labeled methoxy-X04 show that it enters rat brain in amounts that suggest it is a viable candidate as a positron emission tomography (PET) amyloid-imaging agent for in vivo human studies.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
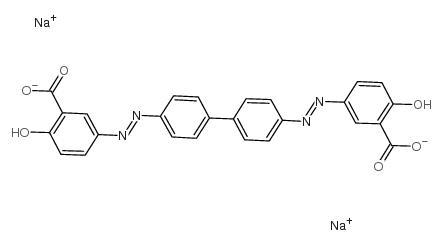 |
CHRYSAMINE G
CAS:6472-91-9 |
C26H16N4Na2O6 |
|
Amyloid binding ligands as Alzheimer's disease therapies.
2002-01-01 [Neurobiol. Aging 23 , 1039-1042, (2002)] |
|
Chrysamine G and its derivative reduce amyloid beta-induced ...
2002-11-15 [Neurosci. Lett. 333 , 5-8, (2002)] |
|
99mTc-MAMA-chrysamine G, a probe for beta-amyloid protein of...
1999-11-01 [Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 26(11) , 1392-9, (1999)] |
|
Inhibition of polyglutamine aggregation in R6/2 HD brain sli...
2001-12-01 [Neurobiol. Dis. 8(6) , 1017-26, (2001)] |
|
In vitro drug treatments reduce the deleterious effects of a...
2012-01-01 [Neurobiol. Dis. 45 , 508-18, (2012)] |