| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
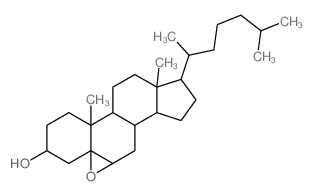 |
(3-beta,5-beta,6-beta)-5,6-Epoxycholestan-3-ol
CAS:4025-59-6 |
|
 |
Cholesterol-5α,6α-epoxide
CAS:1250-95-9 |