| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
S-sulfo-L-cysteine
CAS:1637-71-4 |
|
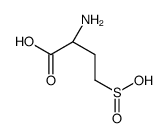 |
D-HOMOCYSTEINESULFINIC ACID
CAS:33514-39-5 |
|
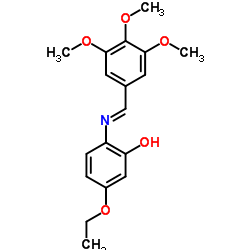 |
l-homocysteinesulfinic acid
CAS:2686-70-6 |