Antifungal synergistic effect of scopoletin, a hydroxycoumarin isolated from Melia azedarach L. fruits.
María C Carpinella, Carlos G Ferrayoli, Sara M Palacios
Index: J. Agric. Food Chem. 53(8) , 2922-7, (2005)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
In the continuous search for antifungal compounds from plants, the hydroxycoumarin scopoletin (1) was isolated from seed kernels of Melia azedarach L. from which three other compounds, vanillin (2), 4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamaldehyde (3), and (+/-) pinoresinol (4), have also been isolated. Guided fractionation through autobiography on TLC using Fusarium verticillioides (Saccardo) Nirenberg as test organism led to the isolation of 1, which exhibited a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 1.50 mg/mL in the microbroth dilution method. Despite its own weak activity, when the coumarin was combined with the above-mentioned compounds, a strong enhancement of the antifungal effect was observed, even showing a complete inhibition in the growth of the pathogen when 1 was added at a concentration of up to 5% of its MIC value. The same level of effectiveness was observed when the synthetic antifungal agents Mancozeb and Carboxin were each combined with compounds 1-4, in which cases it became possible to decrease the effective concentrations of these commercial compounds by up to 2.5 and 3%, respectively.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
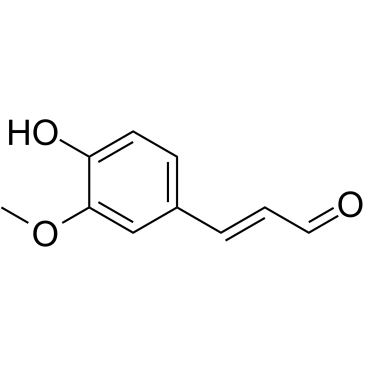 |
coniferyl aldehyde
CAS:458-36-6 |
C10H10O3 |
|
A derivatization and validation strategy for determining the...
2014-08-01 [J. Mass Spectrom. 49(8) , 665-73, (2014)] |
|
Reagent precoated targets for rapid in-tissue derivatization...
2011-08-01 [J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 22(8) , 1409-19, (2011)] |
|
Chemical constituents of Cinnamomum cebuense.
2013-05-01 [Chin. J. Nat. Med. 11(3) , 264-8, (2013)] |
|
Synthesis and evaluation of biological properties of benzyli...
2006-06-01 [Arch. Pharm. Res. 29(6) , 469-75, (2006)] |
|
Molecular cloning and biochemical characterization of two ci...
2013-09-01 [Plant Physiol. Biochem. 70 , 133-41, (2013)] |