The development and application of a new affinity partitioning system for enzyme isolation and purification.
A L Nguyen, J H Luong
Index: Enzyme Microb. Technol. 12 , 663, (1990)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A reactive water-soluble polymer was synthesized by copolymerizing N-isopropylacrylamide and glycidyl acrylate. The reactive polymer could react with the amino groups of enzymes/proteins or other ligands to form an affinity polymer. As a model, the reactive polymer was allowed to react with paraaminobenzamidine, a strong trypsin inhibitor. The affinity polymer could easily form an aqueous two-phase system with either dextran or pullulan, and the phase diagram was compared favorably to that of the well-known polyethylene glycol-dextran system. Once trypsin was attracted to the affinity polymer dominant phase, the enzyme could be dissociated from the polymer at low pH. Owing to the N-isopropylacrylamide units, the affinity polymer could be isolated from the solution by precipitation at a low level of ammonium sulfate. The enzyme recovery was always greater than 50%, and the affinity polymer could be reused in several cycles of affinity partitioning and recovery.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
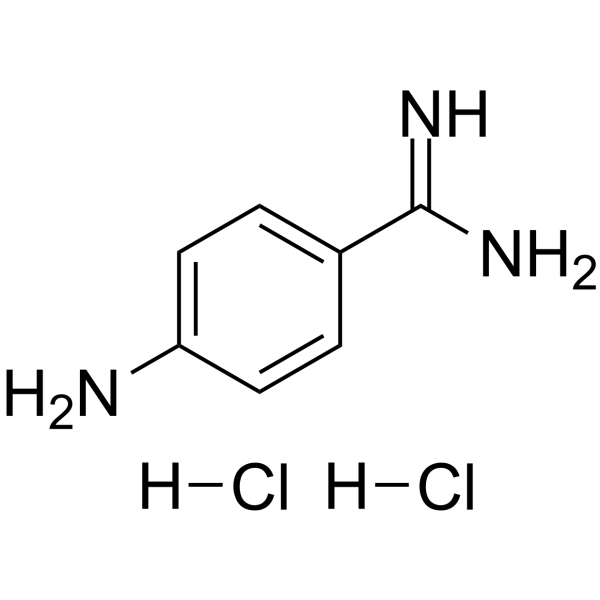 |
4-Aminobenzamidine dihydrochloride
CAS:2498-50-2 |
C7H11Cl2N3 |
|
Comparative study on the inhibition of plasmin and delta-pla...
2015-02-13 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 457(3) , 358-62, (2015)] |
|
p-Aminobenzamidine as a fluorescent probe for the active sit...
1982-03-25 [J. Biol. Chem. 257 , 3014, (1982)] |
|
Comparative studies on the inhibition of trypsin, plasmin, a...
1968-12-05 [Eur. J. Biochem. 6 , 502, (1968)] |
|
STUDIES ON THE ACTIVE CENTER OF TRYPSIN. THE BINDING OF AMID...
1965-04-01 [J. Biol. Chem. 240 , 1579, (1965)] |
|
Specific adsorption of serine proteases on coated silica bea...
[J. Chromatogr. A. 510 , 123, (1990)] |