Second-order advantage with excitation-emission fluorescence spectroscopy and a flow-through optosensing device. Simultaneous determination of thiabendazole and fuberidazole in the presence of uncalibrated interferences.
Gisela N Piccirilli, Graciela M Escandar
Index: Analyst 135(6) , 1299-308, (2010)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
This paper presents a novel approach for the simultaneous determination of two widely used fungicides in a very interfering environment, combining the advantage of a spectrofluorimetric optosensor coupled to a flow-injection system and the selectivity of second-order chemometric algorithms. The sensor is based on the simultaneous retention of thiabendazole and fuberidazole on C18-bonded phase placed inside a flow-cell. After the arrival of the analytes to the sensing zone, the flow is stopped and the excitation-emission fluorescence matrix is read in a fast-scanning spectrofluorimeter. Parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC) and unfolded and multidimensional partial least-squares coupled to residual bilinearization (U- and N-PLS/RBL) were selected for data processing. These algorithms achieve the second-order advantage, and are in principle able to overcome the problem of the presence of unexpected interferences. The power of U-PLS/RBL to quantify both fungicides at parts-per-billion levels, even in the presence of high concentrations of spectral interferences such as carbaryl, carbendazim and 1-naphthylacetic acid, is demonstrated. Indeed, U-PLS/RBL allowed us to reach selectivity using a commercial but non-selective sensing support. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time the potentiality of the 'second-order advantage' is evaluated on a flow-injection system, using an unspecific supporting material and in the presence of three real interferences. Using a sample volume of 2 mL, detection limits of 4 ng mL(-1) and 0.3 ng mL(-1) for thiabendazole and fuberidazol were respectively obtained in samples without interferences. In samples containing interferences, the limits of detection were 17 and 1 ng mL(-1) for thiabendazole and fuberidazol, respectively. The sample frequency, including excitation/emission fluorescence matrix measurements, was 12 samples h(-1). The sensor was satisfactorily applied to the determination of both analytes in real water samples.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
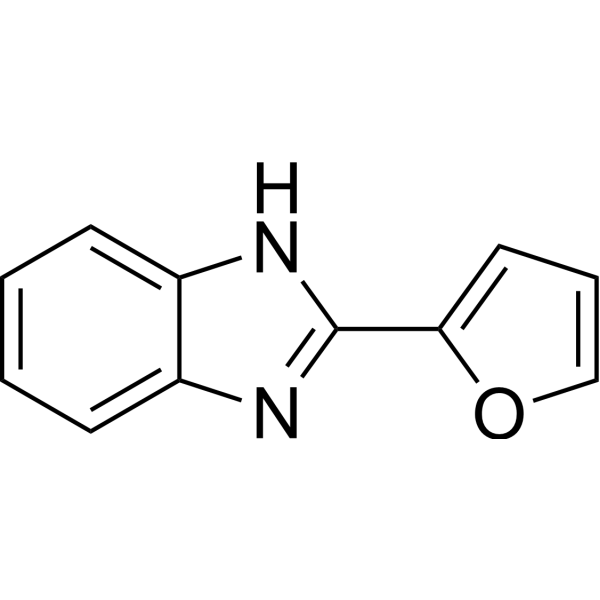 |
Fuberidazole
CAS:3878-19-1 |
C11H8N2O |
|
Subtype-selectivity of metal-dependent methionine aminopepti...
2010-07-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20 , 4038-44, (2010)] |
|
Metal-mediated inhibition of Escherichia coli methionine ami...
2006-01-26 [J. Med. Chem. 49 , 511-22, (2006)] |
|
Quantitative Fusarium spp. and Microdochium spp. PCR assays ...
2007-06-01 [J. Appl. Microbiol. 102(6) , 1645-53, (2007)] |
|
Possible bitertanol and fuberidazole poisoning in young phea...
2001-07-28 [Vet. Rec. 149(4) , 118-20, (2001)] |
|
Determination of benzimidazolic fungicides in fruits and veg...
2009-09-21 [Anal. Chim. Acta 650(2) , 207-13, (2009)] |