Epac and phospholipase Cepsilon regulate Ca2+ release in the heart by activation of protein kinase Cepsilon and calcium-calmodulin kinase II.
Emily A Oestreich, Sundeep Malik, Sanjeewa A Goonasekera, Burns C Blaxall, Grant G Kelley, Robert T Dirksen, Alan V Smrcka
Index: J. Biol. Chem. , 1514-22, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Recently, we identified a novel signaling pathway involving Epac, Rap, and phospholipase C (PLC)epsilon that plays a critical role in maximal beta-adrenergic receptor (betaAR) stimulation of Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release (CICR) in cardiac myocytes. Here we demonstrate that PLCepsilon phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolytic activity and PLCepsilon-stimulated Rap1 GEF activity are both required for PLCepsilon-mediated enhancement of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release and that PLCepsilon significantly enhances Rap activation in response to betaAR stimulation in the heart. Downstream of PLCepsilon hydrolytic activity, pharmacological inhibition of PKC significantly inhibited both betaAR- and Epac-stimulated increases in CICR in PLCepsilon+/+ myocytes but had no effect in PLCepsilon-/- myocytes. betaAR and Epac activation caused membrane translocation of PKCepsilon in PLCepsilon+/+ but not PLCepsilon-/- myocytes and small interfering RNA-mediated PKCepsilon knockdown significantly inhibited both betaAR and Epac-mediated CICR enhancement. Further downstream, the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CamKII) inhibitor, KN93, inhibited betaAR- and Epac-mediated CICR in PLCepsilon+/+ but not PLCepsilon-/- myocytes. Epac activation increased CamKII Thr286 phosphorylation and enhanced phosphorylation at CamKII phosphorylation sites on the ryanodine receptor (RyR2) (Ser2815) and phospholamban (Thr17) in a PKC-dependent manner. Perforated patch clamp experiments revealed that basal and betaAR-stimulated peak L-type current density are similar in PLCepsilon+/+ and PLCepsilon-/- myocytes suggesting that control of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release, rather than Ca2+ influx through L-type Ca2+ channels, is the target of regulation of a novel signal transduction pathway involving sequential activation of Epac, PLCepsilon, PKCepsilon, and CamKII downstream of betaAR activation.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
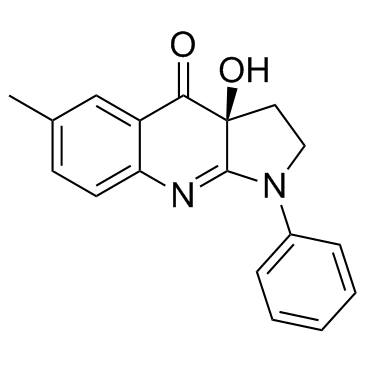 |
(-)-Blebbistatin
CAS:856925-71-8 |
C18H16N2O2 |
|
Stretch-stimulated glucose transport in skeletal muscle is r...
2015-02-01 [J. Physiol. 593(3) , 645-56, (2015)] |
|
Formation of contractile networks and fibers in the medial c...
2015-01-01 [Cytoskeleton (Hoboken.) 72(1) , 29-46, (2015)] |
|
Intramolecular loop/tail interactions are essential for conn...
2010-11-01 [FASEB J. 24 , 4378-95, (2010)] |
|
Glucocorticoid receptor-mediated expression of caldesmon reg...
2008-11-07 [J. Biol. Chem. , 31183-96, (2008)] |
|
Distinct cytoskeleton populations and extensive crosstalk co...
2011-04-01 [Development 138 , 1631-41, (2011)] |