| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
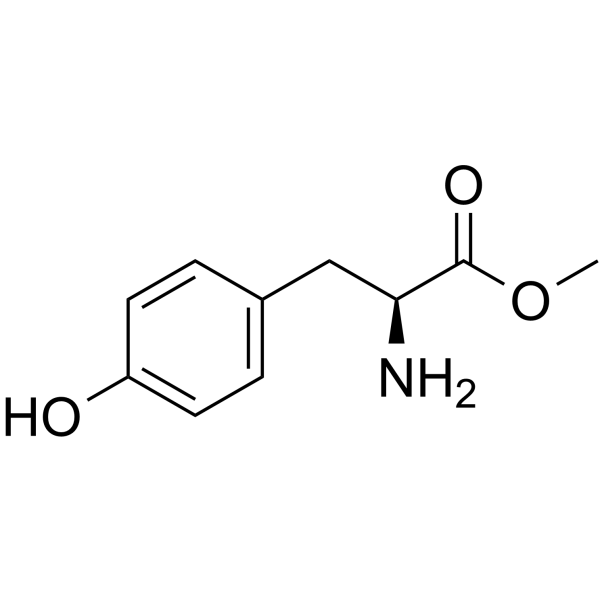 |
H-Tyr-OMe
CAS:1080-06-4 |
|
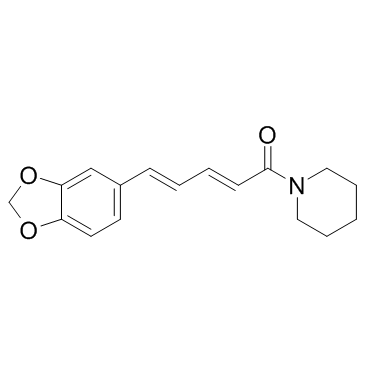 |
Piperine
CAS:94-62-2 |
|
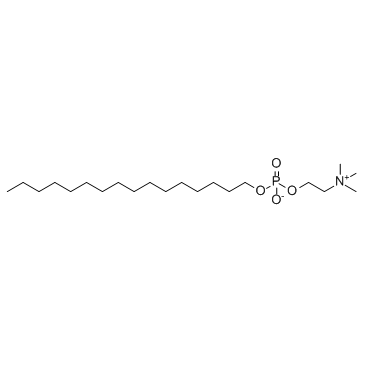 |
Miltefosine
CAS:58066-85-6 |