| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
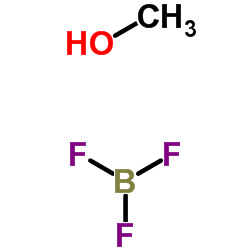 |
Boron trifluoride-methanol
CAS:373-57-9 |
|
 |
Ritalinic acid
CAS:19395-41-6 |
|
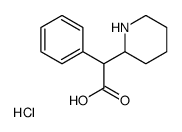 |
alpha-Phenyl-2-piperidineacetic acid hydrochloride
CAS:19395-40-5 |