| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
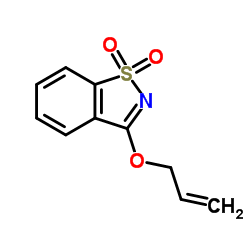 |
3-(Allyloxy)-1,2-benzothiazole 1,1-dioxide
CAS:27605-76-1 |
|
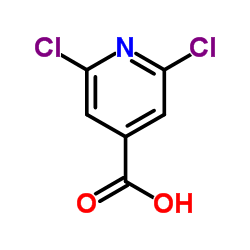 |
2,6-Dichloroisonicotinic acid
CAS:5398-44-7 |