| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
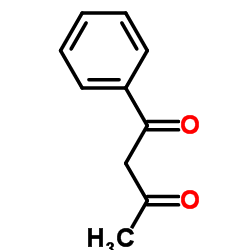 |
1-Phenylbutane-1,3-dione
CAS:93-91-4 |
|
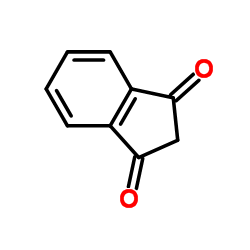 |
1,3-INDANDIONE
CAS:606-23-5 |
|
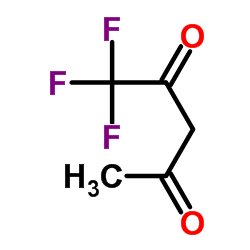 |
1,1,1-Trifluoroacetylacetone
CAS:367-57-7 |