| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
DEQUALINIUM IODIDE
CAS:2019-42-3 |
|
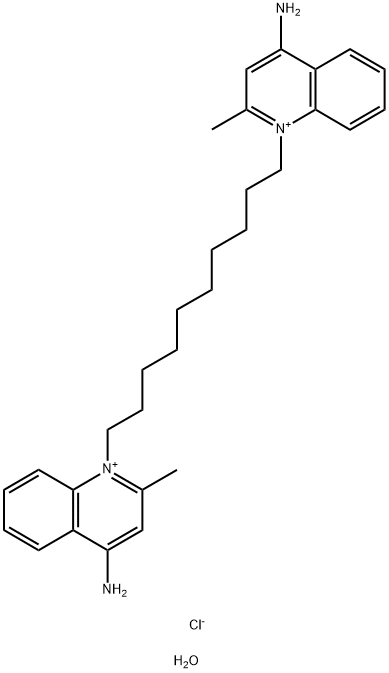 |
Dequalinium chloride hydrate
CAS:1255077-34-9 |
|
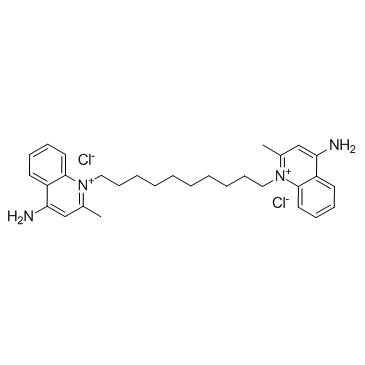 |
Dequalinium Chloride
CAS:522-51-0 |