Isolation of an antimicrobial compound from Impatiens balsamina L. using bioassay-guided fractionation.
X Yang, D K Summerhurst, S F Koval, C Ficker, M L Smith, M A Bernards
Index: Phytother Res. 15(8) , 676-80, (2001)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
By using brine shrimp (Artemia salina) lethality test-guided fractionation, a single bioactive compound (LC(50)=26 ppm) was isolated from the 95% ethanol extract of the dried aerial parts of Impatiens balsamina L. and subsequently identified as 2-methoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone (MNQ). The structure of MNQ was confirmed by UV, FT-IR, MS, and 1-and 2-D NMR spectroscopy. The antimicrobial activity of MNQ was evaluated using 12 bacterial and eight fungal strains. Five gram-positive and two gram-negative bacteria as well as all eight fungi (including multi-drug resistant strains) tested were highly sensitive to MNQ. A tea prepared according to traditional methods was found to contain sufficient MNQ to account for its antimicrobial properties.Copyright 2001 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
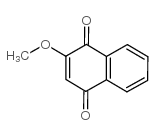 |
Lawsone methyl ether
CAS:2348-82-5 |
C11H8O3 |
|
2-Methoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone (MNQ) induces apoptosis of A549...
2015-08-15 [Life Sci. 135 , 158-64, (2015)] |
|
Anti-gastric adenocarcinoma activity of 2-Methoxy-1,4-naphth...
2012-12-01 [Fitoterapia 83(8) , 1336-44, (2012)] |
|
Effects of the compounds 2-methoxynaphthoquinone, 2-propoxyn...
2007-09-01 [Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 66(1) , 45-52, (2007)] |
|
Antipruritic dinaphthofuran-7,12-dione derivatives from the ...
1998-09-01 [J. Nat. Prod. 61(9) , 1126-9, (1998)] |
|
Antifungal activity of lawsone methyl ether in comparison wi...
2011-01-01 [J. Oral. Pathol. Med. 40(1) , 90-6, (2011)] |