Parecoxib is neuroprotective in spontaneously hypertensive rats after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion: a divided treatment response?
Jesper Kelsen, Katrine Kjaer, Gang Chen, Michael Pedersen, Lisbeth Røhl, Jørgen Frøkiaer, Søren Nielsen, Jens R Nyengaard, Lars Christian B Rønn
Index: J. Neuroinflammation 3 , 31, (2007)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Anti-inflammatory treatment affects ischemic damage and neurogenesis in rodent models of cerebral ischemia. We investigated the potential benefit of COX-2 inhibition with parecoxib in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs) subjected to transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAo).Sixty-four male SHRs were randomized to 90 min of intraluminal tMCAo or sham surgery. Parecoxib (10 mg/kg) or isotonic saline was administered intraperitoneally (IP) during the procedure, and twice daily thereafter. Nineteen animals were euthanized after 24 hours, and each hemisphere was examined for mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and COX enzymes by quantitative RT-PCR. Twenty-three tMCAo animals were studied with diffusion and T2 weighted MRI within the first 24 hours, and ten of the SHRs underwent follow-up MRI six days later. Thirty-three SHRs were given 5-bromo-2'-deoxy-uridine (BrdU) twice daily on Day 4 to 7 after tMCAo. Animals were euthanized on Day 8 and the brains were studied with free-floating immunohistochemistry for activated microglia (ED-1), hippocampal granule cell BrdU incorporation, and neuronal nuclei (NeuN). Infarct volume estimation was done using the 2D nucleator and Cavalieri principle on NeuN-stained coronal brain sections. The total number of BrdU+ cells in the dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus was estimated using the optical fractionator.We found a significant reduction in infarct volume in parecoxib treated animals one week after tMCAo (p < 0.03). Cortical ADC values in the parecoxib group were markedly less increased on Day 8 (p < 0.01). Interestingly, the parecoxib treated rats were segregated into two subgroups, suggesting a responder vs. non-responder phenomenon. We found indications of mRNA up-regulation of IL-1beta, IL-6, TNF-alpha and COX-2, whereas COX-1 remained unaffected. Hippocampal granule cell BrdU incorporation was not affected by parecoxib treatment. Presence of ED-1+ activated microglia in the hippocampus was related to an increase in BrdU uptake in the DG.IP parecoxib administration during tMCAo was neuroprotective, as evidenced by a large reduction in mean infarct volume and a lower cortical ADC increment. Increased pro-inflammatory cytokine mRNA levels and hippocampal granule cell BrdU incorporation remained unaffected.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
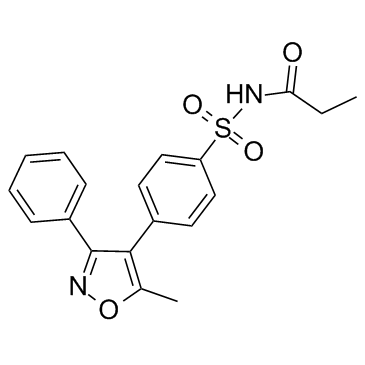 |
parecoxib
CAS:198470-84-7 |
C19H18N2O4S |
|
Bsm1 vitamin D receptor polymorphism and calcium homeostasis...
2015-02-01 [J. Invest. Surg. 28(1) , 8-17, (2015)] |
|
The effect of TSPP-mediated photodynamic therapy and Parecox...
2014-11-11 [Life Sci. 117(2) , 75-83, (2015)] |
|
Prostaglandin-dependent modulation of dopaminergic neurotran...
2016-02-01 [J. Clin. Invest. 126 , 695-705, (2016)] |
|
A randomized controlled trial of preprocedure administration...
2012-01-01 [J. Pain Res. 5 , 251-6, (2012)] |
|
Fast track liver resection: the effect of a comprehensive ca...
2009-01-01 [HPB Surg. 2009 , 271986, (2009)] |