| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
N-Cbz-L-Phenylalanine
CAS:1161-13-3 |
|
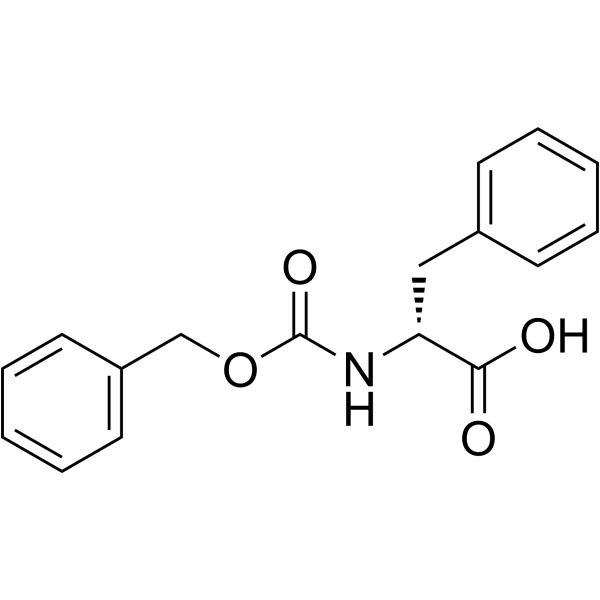 |
Z-D-Phe-OH
CAS:2448-45-5 |