Benzoquinones and terphenyl compounds as phosphodiesterase-4B inhibitors from a fungus of the order Chaetothyriales (MSX 47445).
Tamam El-Elimat, Mario Figueroa, Huzefa A Raja, Tyler N Graf, Audrey F Adcock, David J Kroll, Cynthia S Day, Mansukh C Wani, Cedric J Pearce, Nicholas H Oberlies
Index: J. Nat. Prod. 76(3) , 382-7, (2013)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Three bioactive compounds were isolated from an organic extract of an ascomycete fungus of the order Chaetothyriales (MSX 47445) using bioactivity-directed fractionation as part of a search for anticancer leads from filamentous fungi. Of these, two were benzoquinones [betulinan A (1) and betulinan C (3)], and the third was a terphenyl compound, BTH-II0204-207:A (2). The structures were elucidated using a set of spectroscopic and spectrometric techniques; the structure of the new compound (3) was confirmed via single-crystal X-ray diffraction. Compounds 1-3 were evaluated for cytotoxicity against a human cancer cell panel, for antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans, and for phosphodiesterase (PDE4B2) inhibitory activities. The putative binding mode of 1-3 with PDE4B2 was examined using a validated docking protocol, and the binding and enzyme inhibitory activities were correlated.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
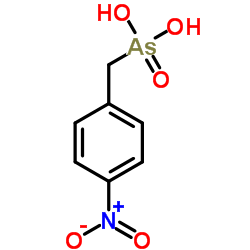 |
3′,5′-Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase
CAS:9040-59-9 |
C7H8AsNO5 |
|
Increase in cellular cyclic AMP concentrations reverses the ...
2013-12-01 [Mol. Pharmacol. 84(6) , 787-93, (2013)] |
|
Regulation of ecto-apyrase CD39 (ENTPD1) expression by phosp...
2013-11-01 [FASEB J. 27(11) , 4419-28, (2013)] |
|
Inhibition of phosphodiesterase-1 attenuates cold-induced pu...
2013-03-01 [Hypertension 61(3) , 585-92, (2013)] |
|
Anchored PDE4 regulates chloride conductance in wild-type an...
2014-02-01 [FASEB J. 28(2) , 791-801, (2014)] |
|
ARL13B, PDE6D, and CEP164 form a functional network for INPP...
2012-11-27 [Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 109(48) , 19691-6, (2012)] |