Therapeutic effect of aspoxicillin on experimental pneumonia with Klebsiella pneumoniae in mice.
T Yamaguchi, N Ishii, K Tani, T Matsushita, K Matsumoto
Index: Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 15(6-7) , 291-6, (1989)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The therapeutic effects of aspoxicillin (ASPC) on an experimental pneumonia in mice were compared with those of piperacillin (PIPC) and mezlocillin (MZPC) under various administration schedules. The pneumonia was induced with K. pneumoniae B-54 by the aerosol method. Fifty mg/kg of each penicillin was subcutaneously injected into mice starting from 12 h after infection. At 3- and 6-h interval regimens, ASPC caused the infected mice to survive longer than the other penicillins. The decrease of viable bacterial counts in the lung after a single or repeated injection of ASPC occurred more rapidly than with the other drugs. The concentration of ASPC in the lung after a single injection was higher than that of the other drugs and the concentration was maintained above the MIC for about 2 h. The therapeutic effects of these penicillins on this model reflected well their concentrations in the lung. Among these penicillins, ASPC gave the highest maximum level and persisted longest in the lung, so is shown to have a therapeutic effect superior to PIPC and MZPC on this model of pneumonia. The findings obtained in this experimental pneumonia model were concluded to correlate well with the good clinical efficacy of ASPC compared to PIPC.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
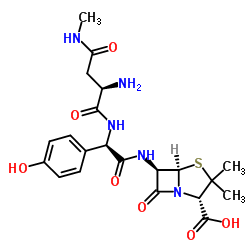 |
Aspoxicillin
CAS:63358-49-6 |
C21H27N5O7S |
|
[In vitro study on efficacy of combination use of aspoxicill...
1992-07-01 [Jpn. J. Antibiot. 45(7) , 763-73, (1992)] |
|
[A clinical study of combined therapy of aspoxicillin and ce...
1992-10-01 [Jpn. J. Antibiot. 45(10) , 1282-94, (1992)] |
|
Separation and determination of aspoxicillin in human plasma...
[J. Chromatogr. A. 515 , 245-55, (1990)] |
|
Antimicrobial susceptibility of Pasteurella multocida isolat...
2001-09-01 [J. Vet. Med. B. Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 48(7) , 555-60, (2001)] |
|
Activity of sub-minimal inhibitory concentrations of aspoxic...
1990-07-01 [J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 26(1) , 29-38, (1990)] |