| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
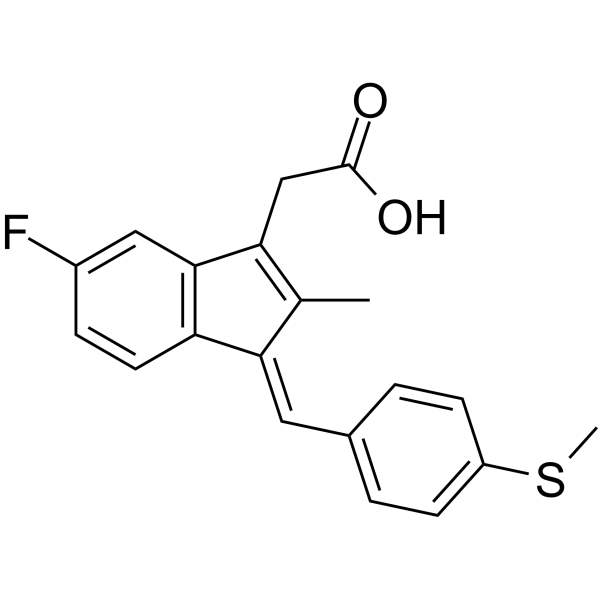 |
Sulindac Sulfide
CAS:32004-67-4 |
|
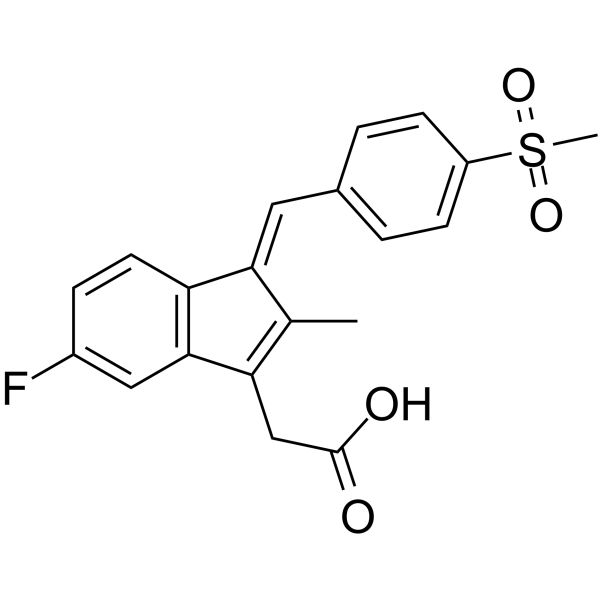 |
Exisulind
CAS:59864-04-9 |