| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
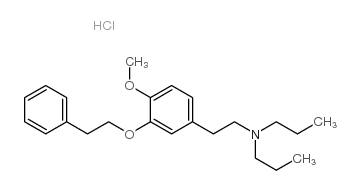 |
NE 100 hydrochloride
CAS:149409-57-4 |
|
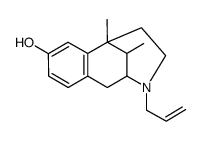 |
SKF-10047
CAS:7619-35-4 |
|
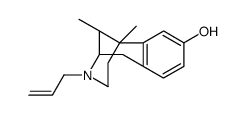 |
n-allylnormetazocine
CAS:14198-28-8 |