Extending levodopa action: COMT inhibition.
P Martínez-Martín, C F O'Brien
Index: Neurology 50(6 Suppl 6) , S27-32; discussion S44-8, (1998)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Degradation of levodopa in the periphery is known to be associated with motor fluctuations and dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease (PD) patients. The enzyme catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) is responsible for much of this degradation. Therefore, inhibiting COMT activity is one method of extending the action of levodopa. The new nitrocatechol-type COMT inhibitors entacapone, nitecapone, and tolcapone inhibit COMT in the periphery; tolcapone also inhibits COMT activity centrally. COMT inhibitors increase patients' duration of response to levodopa and reduce response fluctuations. Administration may prolong levodopa-induced dyskinesia, but peak-dose dyskinesia does not appear to increase. To reduce dyskinesia, the total daily dose of levodopa can be reduced.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
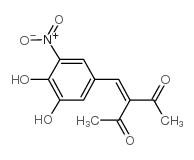 |
Nitecapone
CAS:116313-94-1 |
C12H11NO6 |
|
D1-like dopamine receptor activation and natriuresis by nitr...
2001-05-01 [Kidney Int. 59(5) , 1683-94, (2001)] |
|
The Helicobacter felis mouse model in assessing anti-Helicob...
1996-04-01 [Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 31(4) , 334-8, (1996)] |
|
Nitecapone and selegiline as effective adjuncts to L-DOPA in...
2002-01-01 [Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 24(1) , 23-9, (2002)] |
|
Dopamine is metabolised by different enzymes along the rat n...
2005-06-01 [Pflugers Arch. 450(3) , 185-91, (2005)] |
|
The effect of nitecapone on early graft function in experime...
2000-08-01 [Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 34(4) , 415-20, (2000)] |