| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
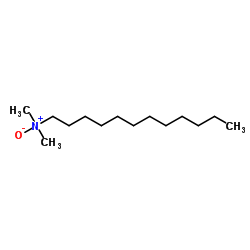 |
N-Dodecyl-N,N-dimethylamine oxide
CAS:1643-20-5 |
|
 |
Magnesium choride
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
 |
Tetraethyleneglycol monooctyl ether
CAS:19327-39-0 |