| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Methyl pyruvate
CAS:600-22-6 |
|
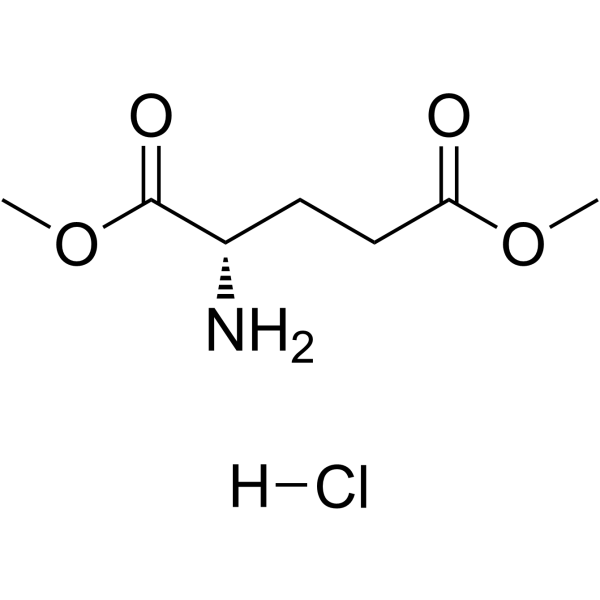 |
H-Glu(OMe)-OMe.HCl
CAS:23150-65-4 |