| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
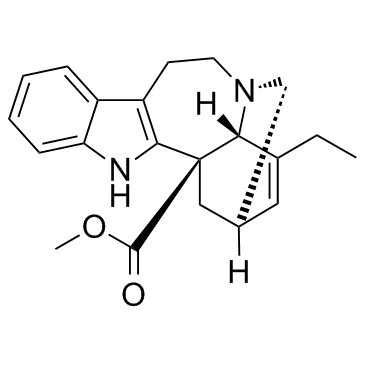 |
Catharanthine
CAS:2468-21-5 |
|
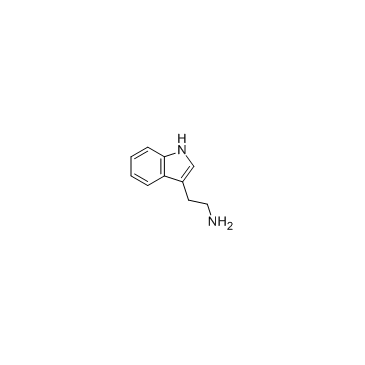 |
tryptamine
CAS:61-54-1 |
|
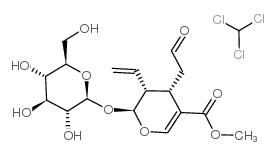 |
Secologanin
CAS:19351-63-4 |
|
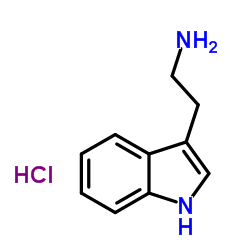 |
2-(1h-indol-3-yl)ethanaminhydrochlorid
CAS:343-94-2 |