Sakuranetin induces adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells through enhanced expression of PPARγ2
Takeshi Saito, Daigo Abe, Keizo Sekiya, Takeshi Saito, Daigo Abe, Keizo Sekiya
Index: Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 372(4) , 835-9, (2008)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Sakuranetin (5,4′-dihydroxy-7-methoxyflavone) belongs to the flavanone class of polyphenols predominantly known as phytoalexin in rice plant. In this study, we demonstrate that sakuranetin strongly induces differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, as evidenced by increased triglyceride accumulation and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPDH) activity. In addition, even in the absence of adipogenic hormonal stimuli, sakuranetin strongly induced adipogenesis and expression of genes that are critical for the adipocytes phenotype. Time-course analyses indicated that sakuranetin induces PPARγ2 expression without prior induction of C/EBPβ, a transcriptional regulator of PPARγ2 in adipogenesis. In 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, the transcriptional factors GATA-2 and GATA-3 are known to down-regulate adipogenesis by direct binding to the C/EBPβ protein and to the GATA-binding site on the PPARγ2 promoter. We found that sakuranetin significantly reduced the expression of GATA-2. Moreover, we observed that sakuranetin stimulated glucose uptake in differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes. These results suggest that sakuranetin may contribute to maintain glucose homeostasis in animals.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
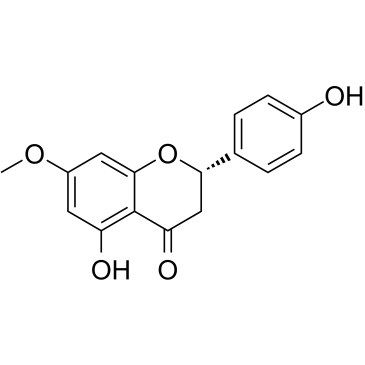 |
Sakuranetin
CAS:2957-21-3 |
C16H14O5 |
|
A nicotinic receptor-mediated anti-inflammatory effect of th...
2014-10-01 [Fitoterapia 98 , 11-21, (2014)] |
|
In vitro antileishmanial and antitrypanosomal activities of ...
2012-02-01 [Exp. Parasitol. 130(2) , 141-5, (2012)] |
|
Isoprenylated flavonoid and adipogenesis-promoting constitue...
2012-04-27 [J. Nat. Prod. 75(4) , 699-706, (2012)] |
|
Induced volatiles in elicitor-treated and rice blast fungus-...
2002-12-01 [Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 66(12) , 2549-59, (2002)] |
|
O-demethylation and sulfation of 7-methoxylated flavanones b...
2003-02-01 [Chem. Pharm. Bull. 51(2) , 203-6, (2003)] |