The in vitro anthelmintic effects of plumbagin on newly excysted and 4-weeks-old juvenile parasites of Fasciola gigantica.
Natcha Lorsuwannarat, David Piedrafita, Pathanin Chantree, Veerawat Sansri, Sineenart Songkoomkrong, Sirasate Bantuchai, Kant Sangpairot, Pornanan Kueakhai, Narin Changklungmoa, Pannigan Chaichanasak, Piyachat Chansela, Prasert Sobhon
Index: Exp. Parasitol. 136 , 5-13, (2014)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The effect of plumbagin (PB, 5-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone) against newly excysted juveniles (NEJs) and 4-weeks-old immature parasites of Fasciola gigantica were compared with triclabendazole (TCZ). The anthelmintic efficacy of 1, 10 and 100μg/ml of PB or TCZ following incubation in vitro for 1-24h was compared using a combination of relative motility (RM), survival index (SI) and larval migration inhibition (LMI) assays for parasite viability. The RM and SI values of the PB-treated group decreased at a more rapid rate than the TCZ-treated group. For NEJs, the decreased RM values were first observed at 1h incubation with 1μg/ml PB, and 90% of flukes were killed at 24h. In contrast, in TCZ-treated groups a 10-fold higher concentration of TCZ (10μg/ml) resulted in only 9% dead parasites after 24h incubation. In 4-weeks-old juvenile parasites, PB reduced the RM value at 10μg/ml with 100% of flukes dead after 3h, while TCZ decreased RM values at the concentration of 100μg/ml but with only 5% of flukes killed at 24h. NEJs treated with PB exhibited 88%, 99% and 100% of LMIs at the concentrations of 1, 10 and 100μg/ml, respectively. NEJs incubated with TCZ have an LMI of only 32% at the highest concentration of 100μg/ml. Similarly PB had a significantly greater killing of immature 4weeks juvenile stages than TCZ at all concentrations; however, 4-weeks-old juvenile parasites were more resistant to killing by PB or TCZ at all concentrations when compared to NEJs. Further studies were carried out to investigate the alterations of the parasite tegument by scanning electron microscope (SEM). PB caused similar tegumental alterations in 4-weeks-old juveniles as those observed in TCZ treatment but with greater damage at comparative time points, comprising of swelling, blebbing and rupture of the tegument, loss of spines, and eventual erosion, lesion and desquamation of the total tegument. These data indicate that PB had a greater fasciolicidal effect against immature stages of F. gigantica parasites than TCZ and warrant further studies for use as a potential new anthelmintic against Fasciola infections. Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
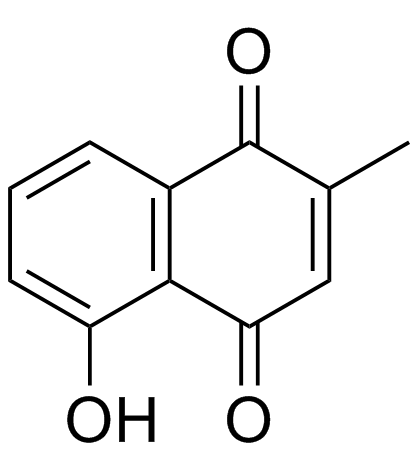 |
Plumbagin
CAS:481-42-5 |
C11H8O3 | |
 |
Triclabendazole
CAS:68786-66-3 |
C14H9Cl3N2OS |
|
Antitumorigenic effect of plumbagin by induction of SH2-cont...
2015-01-01 [Int. J. Oncol. 46 , 2380-8, (2015)] |
|
Binding and Anticancer Properties of Plumbagin with Human Se...
2015-09-01 [Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 86 , 362-9, (2015)] |
|
Inhibition of ANO1/TMEM16A Chloride Channel by Idebenone and...
2015-01-01 [PLoS ONE 10 , e0133656, (2015)] |
|
Posttranslational Regulation of Human DNA Polymerase ι.
2015-11-06 [J. Biol. Chem. 290 , 27332-44, (2015)] |
|
NADPH oxidase 4 is involved in the triethylene glycol dimeth...
2015-07-01 [Clin. Oral Investig. 19 , 1463-71, (2015)] |