Upregulation of MIP-2 (CXCL2) expression by 15-deoxy-Delta(12,14)-prostaglandin J(2) in mouse peritoneal macrophages.
Hyo Y Kim, Hee S Kim
Index: Immunol. Cell Biol. 85(1) , 60-7, (2007)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) ligand, 15-deoxy-Delta(12,14)-prostaglandin J(2) (15d-PGJ(2)), has been reported to possess anti-inflammatory activity in activated monocytes/macrophages. In this study, we investigated the effect of 15d-PGJ(2) on the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced expression of chemokine mRNAs, especially macrophage inhibitory protein (MIP)-2 (CXCL2), in mouse peritoneal macrophages. The inhibitory actions of the natural PPARgamma ligands, 15d-PGJ(2) and prostaglandin A1 (PGA1), on the expression of RANTES (regulated upon activation, normal T expressed and secreted; CCL5), MIP-1beta (CCL4), MIP-1alpha (CCL3), IFN-gamma-inducible protein 10 kilodaltons (IP-10; CXCL10) and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1; CCL2) mRNA in LPS-treated cells were stronger than those of the synthetic PPARgamma ligands troglitazone and ciglitazone. However, 15d-PGJ(2) enhanced the expression of LPS-induced MIP-2 (CXCL2) mRNA. A specific PPARgamma antagonist (GW9662) had no effect on the inhibitory action of 15d-PGJ(2) and PGA1 in LPS-induced chemokine mRNA expression and on the synergistic action of 15d-PGJ(2) in LPS-induced MIP-2 (CXCL2) expression. Moreover, LPS itself reduced the expression of PPARgamma. Although the synergistic effect of 15d-PGJ(2) on LPS-induced MIP-2 (CXCL2) mRNA expression was remarkable, the production of MIP-2 (CXCL2) in cells treated with 15d-PGJ(2) and LPS did not increase compared to the production in cells treated with LPS alone. The synergistic action of 15d-PGJ(2) on LPS-induced MIP-2 (CXCL2) mRNA expression was dependent on the activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB), and 15d-PGJ(2) increased the phosphorylation of p38 and stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (SAPK/JNK) in cells stimulated with LPS. These results suggest that the synergistic effect of 15d-PGJ(2) on LPS-induced MIP-2 (CXCL2) expression is PPARgamma-independent, and is mediated by the p38 and SAPK/JNK pathway in mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways, which activates NF-kappaB. Our data may give more insights into the different mechanisms contrary to the anti-inflammatory effect of 15d-PGJ(2) on the expression of chemokine genes.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
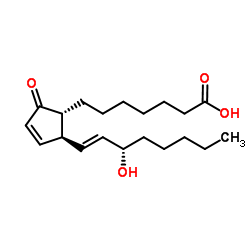 |
PROSTAGLANDIN A1
CAS:14152-28-4 |
C20H32O4 |
|
The cyclopentenone prostaglandin 15d-PGJ2 inhibits the NLRP1...
2015-03-15 [J. Immunol. 194(6) , 2776-85, (2015)] |
|
Protective effects of n-6 fatty acids-enriched diet on intes...
2015-02-01 [Br. J. Pharmacol. 172(3) , 910-23, (2015)] |
|
Vimentin filament organization and stress sensing depend on ...
2015-01-01 [Nat. Commun. 6 , 7287, (2015)] |
|
Transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) channel as em...
2010-07-22 [J. Med. Chem. 53 , 5085-107, (2010)] |
|
TGA transcription factors and jasmonate-independent COI1 sig...
2013-02-01 [J. Exp. Bot. 64(4) , 963-75, (2013)] |