Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications
1985-08-15
A transition-state-analog inhibitor influences zinc-binding by Aeromonas aminopeptidase.
J O Baker, J M Prescott
Index: Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 130(3) , 1154-60, (1985)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The transition-state-analog inhibitor, 1-butaneboronic acid, markedly enhances the uptake of one g-atom of Zn2+ ions from a metal ion buffer system by Zn-depleted Aeromonas aminopeptidase. In contrast, a substrate-analog inhibitor, n-valeramide, does not perturb the equilibrium between Zn2+ ions and the enzyme in a metal ion buffer system. These results establish a role for metal ions in the binding of 1-butaneboronic acid to Aeromonas amino-peptidase and strongly imply that a bound Zn2+ ion interacts directly with substrate during catalysis but not during initial binding of substrate.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
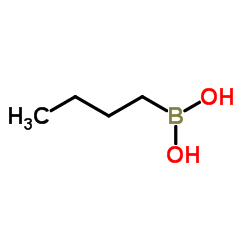 |
1-Butaneboronic acid
CAS:4426-47-5 |
C4H11BO2 |
Related Articles:
More...
|
Inhibitors of bacterialN-succinyl-l,l-diaminopimelic acid de...
2009-01-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 19 , 6350-2, (2009)] |
|
n-Alkylboronic acid inhibitors reveal determinants of ligand...
2014-10-28 [Biochemistry 53(42) , 6679-86, (2014)] |
|
The use of low-energy collisionally activated dissociation n...
1994-03-01 [Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 8(3) , 265-73, (1994)] |
|
Measurement of myo-inositol in diabetic sera by GC/MS/SIM us...
1988-08-31 [Clin. Chim. Acta 176(2) , 207-12, (1988)] |
|
15 beta-hydroxysteroids (Part III). Steroids of the human pe...
1996-01-01 [Steroids 61(1) , 11-7, (1996)] |