Kinetics and mechanism of degradation of lithospermic acid B in aqueous solution.
Yong-Xue Guo, Zhi-Long Xiu, Dai-Jia Zhang, Hui Wang, Long-Xing Wang, Hong-Bin Xiao
Index: J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 43(4) , 1249-55, (2007)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The degradation of lithospermic acid B (LAB) was investigated as a function of buffer concentration, pH and temperature. Stability tests were performed using a stability-indicating high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with UV-vis detection. The degradation followed pseudo-first-order kinetics under all experimental conditions. The maximum stability of LAB was observed at pH 2.0. The logk(pH)-pH profile described by specific acid-base catalysis and water molecules agreed with the experimental results. The overall degradation rate constant as a function of the temperature under the given conditions obeyed the Arrhenius equation. The chemical fate of LAB in mild acidic solution was investigated, and nine degradation products were detected and tentatively identified by LC-MS analysis. The primary degradation pathway involving the cleavage of ester bond and ring-opened of benzofuran in the LAB are proposed.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
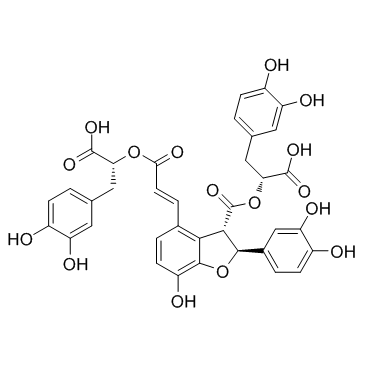 |
salvianolic acid B
CAS:121521-90-2 |
C36H30O16 |
|
Surfactant-coated graphitized multiwalled carbon nanotubes a...
2015-04-01 [Electrophoresis 36(7-8) , 1055-63, (2015)] |
|
Tissue-smashing based ultra-rapid extraction of chemical con...
2014-07-01 [J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 95 , 213-9, (2014)] |
|
The caffeic acid in aqueous extract of Tournefortia sarmento...
2014-12-01 [Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 36(6) , 390-6, (2014)] |
|
Overexpression of allene oxide cyclase promoted tanshinone/p...
2012-12-01 [Plant Cell Rep. 31(12) , 2247-59, (2012)] |
|
Design, synthesis, and discovery of stilbene derivatives bas...
2007-08-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 17 , 4481-6, (2007)] |